BLOG

How to Calculate Your Carbon Footprint: Step-by-Step Guide
How Do I Calculate My Carbon Footprint? A Complete Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction: Why Your Carbon Footprint Matters
When we talk about climate change, we often hear the term “carbon footprint.” But what does it really mean, and why should you care about calculating yours?
Your carbon footprint is essentially the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs)—mainly carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O)—that are emitted into the atmosphere as a result of your actions. This could be from driving a car, heating your home, eating certain foods, manufacturing products, or even using digital services.
Understanding your footprint isn’t just a “green lifestyle” gimmick—it’s a critical step in knowing how much you’re contributing to global emissions and where you can make the biggest impact in reducing them.
If you don’t measure it, you can’t manage it. That’s true for your household, your business, and even at a national level. This guide will help you not only calculate your carbon footprint step-by-step, but also understand the common tools, pitfalls, and ways to take action.
What is a Carbon Footprint?
In simple terms: Your carbon footprint is the sum total of all greenhouse gas emissions you generate, directly and indirectly, over a certain period of time.
-Direct emissions (Scope 1): The emissions you directly cause, such as burning petrol in your car or gas for heating.
-Indirect emissions from energy (Scope 2): Emissions caused by producing the electricity or heat you consume.
-Other indirect emissions (Scope 3): Emissions from the wider supply chain, such as the production of the clothes you buy or the waste you generate.
For example:
-Driving a petrol car emits CO₂ from fuel combustion (Scope 1).
-Using electricity from coal-fired power plants creates emissions indirectly (Scope 2).
-Ordering a fast fashion item shipped from another country adds emissions from manufacturing and transportation (Scope 3).
Why Should You Calculate It?
-
Identify problem areas: Know which activities contribute most to your footprint.
-
Set realistic reduction targets: Data beats guesswork.
-
Track progress: See year-on-year improvement.
-
Meet regulations and certifications: Many businesses require it for ESG reporting or carbon credit eligibility.
-
Support global climate goals: Every ton of CO₂ avoided matters.
Step-by-Step: How to Calculate Your Carbon Footprint
The calculation process is more straightforward than most people think—if you follow a structured approach.
Step 1: Decide the Scope
Are you calculating for:
-An individual? (Personal travel, diet, home energy use)
-A household? (All residents’ combined usage)
-A business or organization? (All operations, supply chain, and product life cycles)
This will determine the level of detail and the type of data you’ll need.
Step 2: Gather Your Data
You’ll need accurate numbers for a given time period (usually a year):
For individuals/households:
-Electricity consumption (kWh from bills)
-Gas, LPG, or heating oil usage
-Water usage
-Car mileage and fuel consumption
-Public transport use (bus, train, metro)
-Flights (number, distance, class)
-Waste generation and recycling rates
-Diet type (meat-heavy, vegetarian, vegan)
For businesses:
-Fuel usage for company vehicles or machinery
-Electricity and heat consumption
-Freight and logistics records
-Employee commuting patterns
-Procurement data for goods and services
-Waste management data
-Production volumes
Step 3: Choose a Calculation Method
There are three main approaches:
1. Activity-based method
-Most accurate.
-Multiply your activity data by official emission factors.
Example: Litres of petrol × CO₂ factor per litre.
2. Spend-based method
-Simpler, uses money spent as a proxy.
Example: ₹10,000 spent on clothing × average emission factor per rupee.
Less precise because prices don’t always reflect carbon intensity.
3. Hybrid method
-Combines both approaches for a more balanced and realistic result.
-Recommended for businesses with partial data.
Step 4: Use a Reliable Calculator or Tool
Some trusted online calculators:
-CarbonFootprint.com – Suitable for individuals and small businesses.
-EPA Carbon Footprint Calculator – U.S.-focused but good for global estimates.
-Nature Conservancy’s Calculator – User-friendly, for individuals.
-Gold Standard Tools – Often used for project verification in carbon credit markets.
-Custom dMRV tools – For businesses, use tech platforms (like Anaxee’s Climate Command Centre) for ongoing tracking.
Step 5: Apply the Formula
The general equation is:
Carbon footprint = Activity data × Emission factor
Example for car travel:
-You drive 15,000 km/year.
-Your car consumes 6 litres per 100 km → 900 litres/year.
-Emission factor for petrol ≈ 2.31 kg CO₂/litre.
Result: 900 × 2.31 = 2,079 kg CO₂/year (≈ 2.08 tons CO₂).
Step 6: Sum It Up
Add all categories: energy use, transport, waste, products, and services. This gives you your total annual carbon footprint.
Real-World Examples
-Average Indian footprint: ~2 tons CO₂ per person/year.
-Global average: ~4.7 tons CO₂/year.
-U.S. average: ~16 tons CO₂/year.
A single return flight from Delhi to London in economy can add over 1 ton of CO₂ to your personal total.
Common Pitfalls in Calculation
-Incomplete data – Estimating too much leads to inaccuracy.
-Ignoring Scope 3 emissions – This often forms the majority for businesses.
-Using outdated emission factors – Always use the latest from recognized sources.
-Over-relying on spend-based methods – They mask real differences in carbon intensity.
Beyond Measurement: How to Reduce Your Footprint
-
Switch to renewable energy – Solar, wind, or certified green electricity.
-
Travel smart – Use public transport, carpool, or go electric.
-
Change your diet – Reduce meat, especially beef and lamb.
-
Buy less, buy better – Opt for quality, long-lasting goods.
-
Waste less – Repair, reuse, recycle.
-
Offset what’s left – Invest in verified carbon offset projects.
Business Benefits of Carbon Accounting
For organizations, calculating and reporting your carbon footprint can:
-Improve brand image and customer trust.
-Reduce operational costs through efficiency.
-Meet regulatory requirements.
-Access green finance or carbon markets.
-Strengthen ESG reporting.
Tools & Standards Worth Knowing
-GHG Protocol – The global standard for GHG accounting.
-ISO 14064 – International standard for emissions reporting.
-Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) – For product-level carbon footprints.
Call to Action
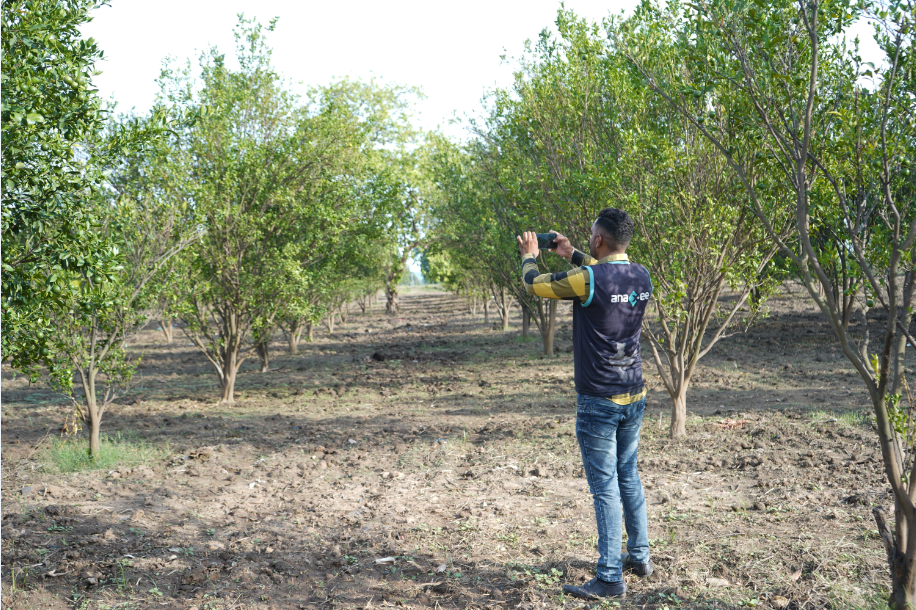
At Anaxee, we help individuals, corporates, and project developers measure, monitor, and reduce carbon footprints using our on-ground data collection and digital monitoring tools. Whether you want to understand your own footprint or track it across a large-scale project, we can make it accurate, transparent, and actionable.
Ready to measure yours?
Start with a trusted calculator today—and take your first step toward a smaller footprint.
About Anaxee:
Anaxee drives large-scale, country-wide Climate and Carbon Credit projects across India. We specialize in Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) and community-driven initiatives, providing the technology and on-ground network needed to execute, monitor, and ensure transparency in projects like agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, improved cookstoves, solar devices, water filters and more. Our systems are designed to maintain integrity and verifiable impact in carbon methodologies.
Beyond climate, Anaxee is India’s Reach Engine- building the nation’s largest last-mile outreach network of 100,000 Digital Runners (shared, tech-enabled field force). We help corporates, agri-focused companies, and social organizations scale to rural and semi-urban India by executing projects in 26 states, 540+ districts, and 11,000+ pin codes, ensuring both scale and 100% transparency in last-mile operations.