BLOG

Rock Weathering: A Natural Climate Solution Transforming Carbon Removal
Rock Weathering: A Natural Climate Solution Transforming Carbon Removal
Introduction: Why We Need to Look Beneath Our Feet
As climate change accelerates, the urgency to remove carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere has intensified. Governments, companies, and climate scientists are searching for scalable, affordable, and permanent solutions. Among nature-based and tech-assisted methods, one solution that’s gaining traction yet remains under-discussed is “rock weathering.” This naturally occurring geological process may not sound revolutionary, but its potential to sequester billions of tonnes of carbon is drawing serious attention.
India, too, with its vast basaltic formations and mineral-rich terrain, is uniquely positioned to lead in the application of this method — especially with the emergence of Article 6 mechanisms and India’s own Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS). But before we get to the market opportunities, let’s understand what rock weathering actually is.
1. What is Rock Weathering?
Rock weathering is the natural process by which rocks break down over time due to exposure to air, water, and biological activity. When it comes to climate, we are specifically interested in a sub-type called “chemical weathering” — particularly of silicate minerals.
Here’s how it works:
-Silicate rocks (like basalt or olivine) react with atmospheric CO₂ and rainwater.
-This forms bicarbonates, which are eventually washed into the oceans.
-Over thousands of years, the bicarbonates turn into carbonates and are stored in marine sediments — effectively locking away CO₂.
This process has been regulating Earth’s climate for millions of years, but it operates on geological timeframes. What’s new is the idea of “enhanced weathering.”
2. Enhanced Weathering: Speeding Up a Natural Process
Enhanced weathering is a climate intervention technique that aims to accelerate this natural CO₂ removal process by:
-Crushing silicate rocks to increase surface area
-Spreading them over farmland, grasslands, or degraded land
-Letting rainfall and soil processes do the rest
One of the key advantages is that this method is permanent, meaning the captured carbon doesn’t get released back into the atmosphere like in many short-term offset projects. And it does not require massive infrastructure.
Think of it as turning crushed rock into a carbon sponge.
3. The Science Behind It
The chemical formula for the reaction is often simplified like this:
This means one molecule of silicate binds with one molecule of CO₂ to form solid calcium carbonate and silica.
Some popular rocks for this purpose include:
-Olivine – Found in dunite, highly reactive with CO₂
-Basalt – Abundant in India’s Deccan Plateau
-Peridotite – Found in ophiolites, very high in magnesium silicates
The key is the reaction kinetics — how fast the rocks weather in a given climate and soil condition. Humid tropical environments like India offer excellent conditions for faster weathering.
4. Agronomic Co-benefits: More Than Just Carbon
Interestingly, this approach doesn’t just sequester carbon. It also improves soil health:
-Reduces soil acidity – A natural liming effect, particularly helpful in acidic soils
-Adds nutrients – Basalt contains potassium, calcium, and magnesium
-Improves water retention – Microporous crushed rock increases soil capacity
-Boosts crop yields – Some early studies show 5–10% increase in output
This makes it ideal for integrating with agricultural programs, especially in smallholder farming systems like India’s. Enhanced rock weathering could serve dual purposes: climate mitigation and rural soil rejuvenation.
5. Potential in India: A Hidden Advantage
India’s geology offers one of the largest contiguous basalt formations in the world — the Deccan Traps, spanning Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and parts of Telangana and Karnataka. These rocks are not just abundant but also underutilized.
Why India is Strategically Positioned:
| Factor | India’s Advantage |
| Rock Availability | Extensive basalt from Deccan Trap |
| Climate Suitability | Monsoonal rains, warm temperatures |
| Agricultural Integration | Smallholder farms, acidic soils in many regions |
| Labor Force | Rural outreach potential for spreading material |
| Policy Environment | CCTS and Voluntary Carbon Market reforms |
If India scales this approach regionally, it could create a climate-positive agri-revolution.
6. Rock Weathering vs. Other Carbon Removal Methods
Let’s compare rock weathering with some other popular carbon removal approaches:
| Approach | Cost (USD/tCO₂) | Permanence | Co-benefits | Maturity |
| Rock Weathering | $50–$150 | 1,000+ yrs | Soil, yield | Emerging |
| Biochar | $30–$120 | 100–500 yrs | Soil fertility | Mature |
| DAC (Direct Air Capture) | $600–$1000+ | 1,000+ yrs | None | Nascent |
| Afforestation | $10–$50 | Decades | Biodiversity | Mature |
| Soil Carbon | $15–$50 | Short-term | Agronomic benefits | Mature |
What stands out is the permanence of rock weathering — it offers high-integrity carbon removal without the risk of reversal.
7. Current Research and Pilot Projects
Globally, organizations like UNDO (UK), Project Vesta (US), and Lithos Carbon (US) are conducting large-scale field trials. Some early learnings include:
-Fine particle size increases weathering speed
-Optimal pH and microbial activity boost CO₂ capture
-Yield gains create additional incentives for farmers
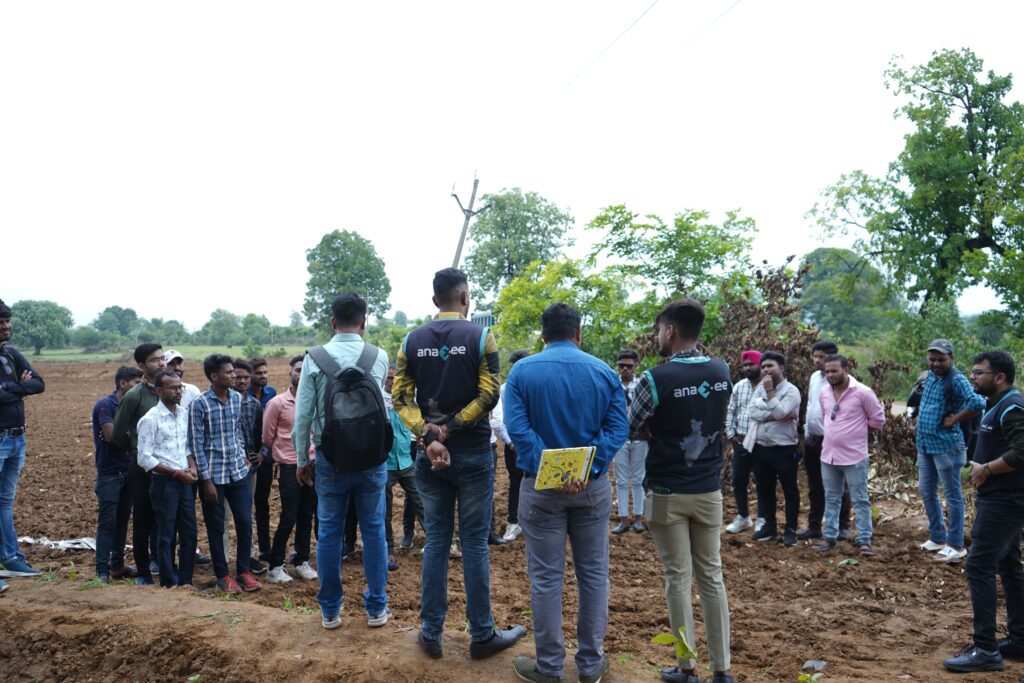
In India, few pilots are underway — mostly in Karnataka and Maharashtra, often piggybacking on regenerative agriculture or CSR programs. The current bottleneck? Lack of awareness, field-level deployment partners, and MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, Verification) frameworks.
This is where outreach-focused organizations like Anaxee can play a crucial role.
8. MRV for Rock Weathering: The Tech Challenge
Measuring how much CO₂ has been captured through rock weathering isn’t straightforward. It requires:
-Soil and water sampling – Bicarbonate concentrations, pH shifts
-Isotope tracing – Carbon isotopes to confirm geological origin
-Modeling weathering rates – Using geochemical software like PHREEQC
-Remote sensing and AI – For monitoring deployment and crop impact
Emerging dMRV platforms can help digitize this — using drone surveys, soil sensors, and machine learning to predict and verify CO₂ sequestration.
9. Policy and Carbon Market Integration
Enhanced rock weathering is already recognized by:
-IPCC as a negative emissions technology
-Puro.earth as a certifiable carbon removal methodology
-Verra is in the process of developing weathering protocols
-CCTS (India) can enable voluntary issuance in a co-benefit-linked framework
As India’s carbon market matures under Article 6.2 and 6.4, early projects in rock weathering can be positioned for future trading. Particularly if India adopts a separate track for durable carbon removals — as seen in the EU and US.
10. Risks and Criticism: A Balanced View
No solution is perfect. Rock weathering faces challenges:
-Dust inhalation – Crushed rocks need safe handling protocols
-Energy use – Crushing rocks consumes energy; needs renewable power
-Ecological impact – Mining new rock could harm ecosystems
-Measurement uncertainty – Requires sophisticated MRV, still evolving
Mitigation involves using mine tailings, renewable-powered crushing, and targeting degraded land for spreading.
11. What’s Next: The Road to Scale
Here’s how this can move from pilot to large-scale deployment in India:
-
Mapping basalt deposits – Government geological surveys + remote sensing
-
Farmer partnerships – Particularly in acidic-soil districts
-
Integration with CSR/NbS – Projects by corporates looking for removals
-
MRV stack development – With tech partners and carbon platforms
-
Carbon credit registration – Either with Verra, Gold Standard, or future Indian registries
Anaxee, with its rural last-mile capabilities and tech-enabled tracking, is well placed to be an execution partner in this new frontier.
Conclusion: Turning Rocks into a Climate Asset
Rock weathering represents the fusion of deep-time geology with cutting-edge climate science. It’s quiet, solid, and permanent- just like the rocks themselves. And it could turn India’s volcanic past into a climate-secure future.
As the carbon market shifts toward durable removals, enhanced rock weathering offers India a rare opportunity: to lead the world by deploying a homegrown, natural climate solution — quite literally — from the ground up.
About Anaxee:
Anaxee drives large-scale, country-wide Climate and Carbon Credit projects across India. We specialize in Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) and community-driven initiatives, providing the technology and on-ground network needed to execute, monitor, and ensure transparency in projects like agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, improved cookstoves, solar devices, water filters and more. Our systems are designed to maintain integrity and verifiable impact in carbon methodologies.
Beyond climate, Anaxee is India’s Reach Engine- building the nation’s largest last-mile outreach network of 100,000 Digital Runners (shared, tech-enabled field force). We help corporates, agri-focused companies, and social organizations scale to rural and semi-urban India by executing projects in 26 states, 540+ districts, and 11,000+ pin codes, ensuring both scale and 100% transparency in last-mile operations.

Ready to collaborate on your next Climate or Carbon project?
Email us at:sales@anaxee-wp-aug25-wordpress.dock.anaxee.com