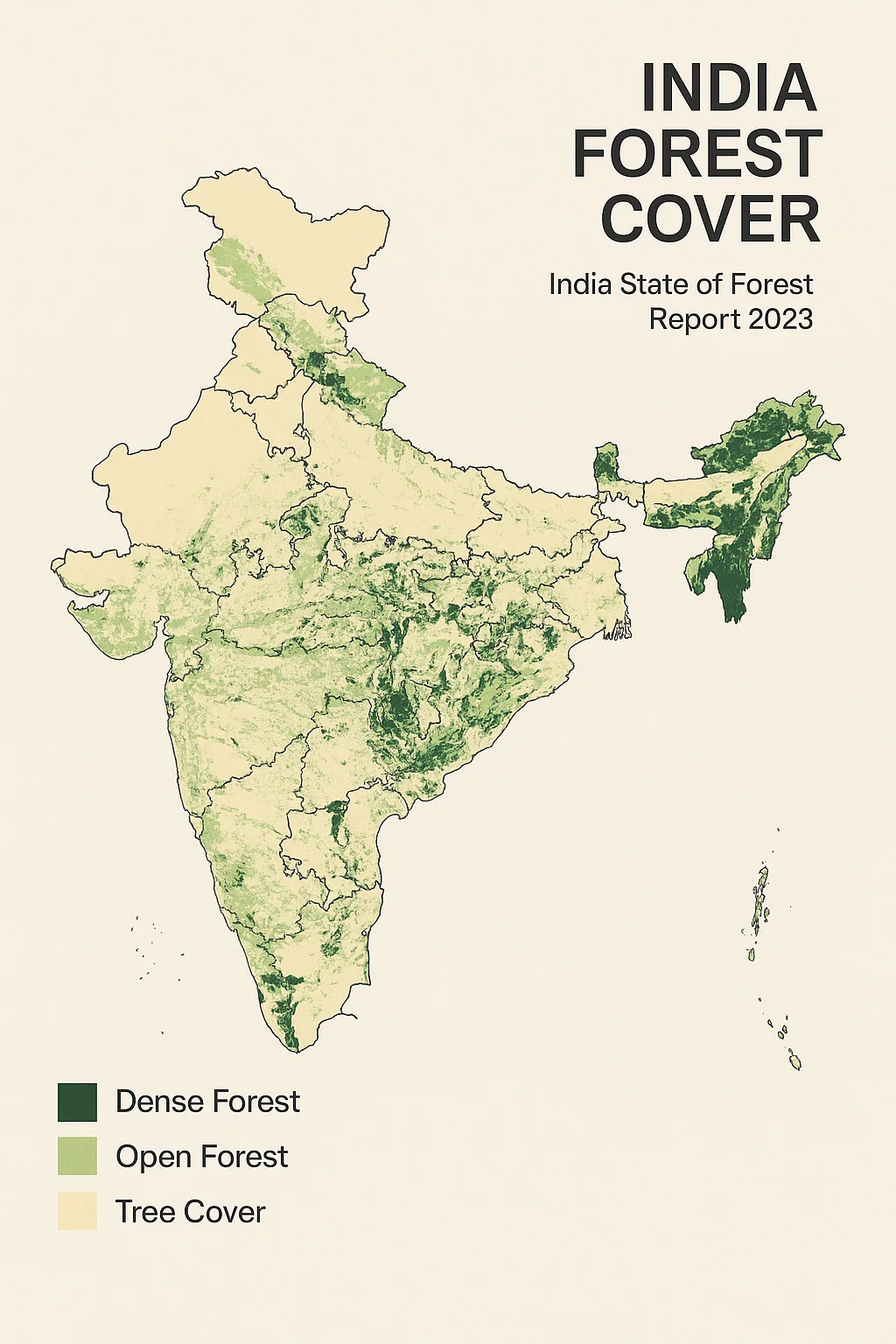
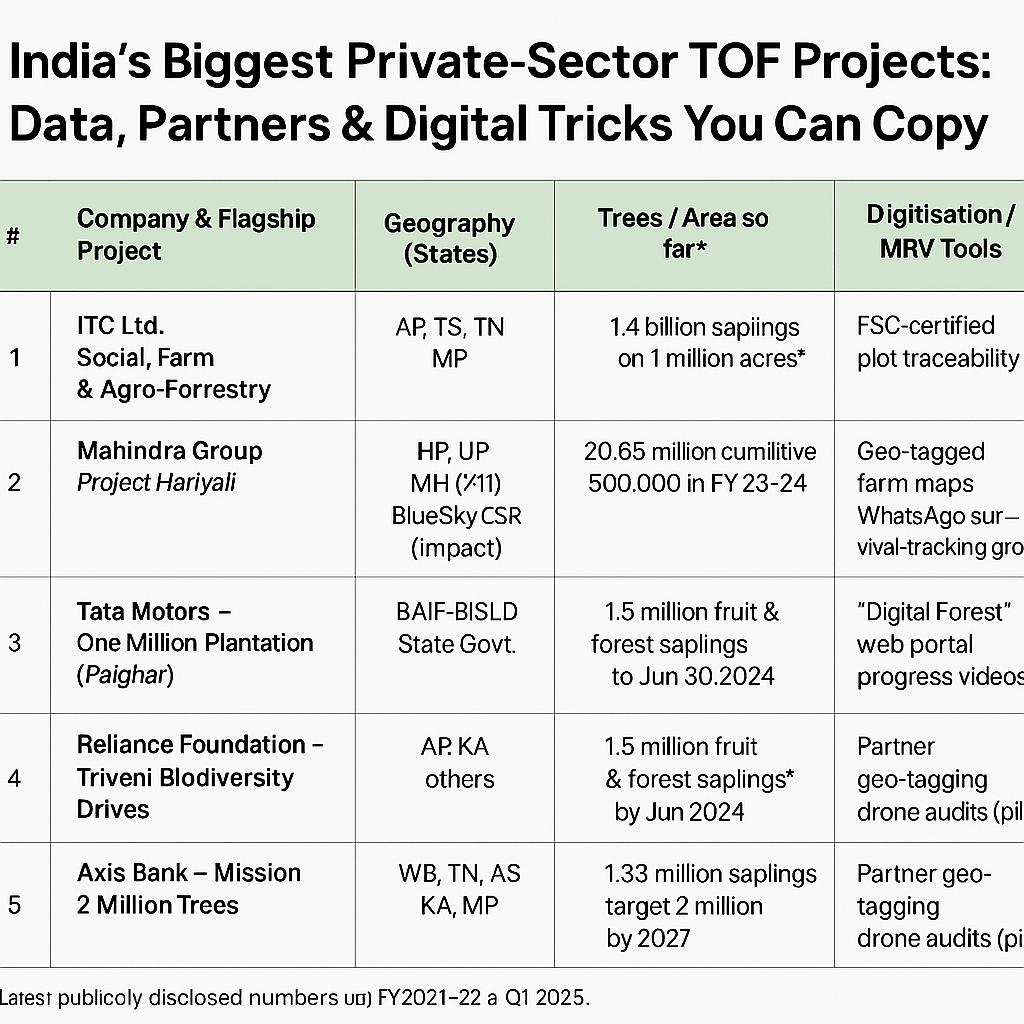
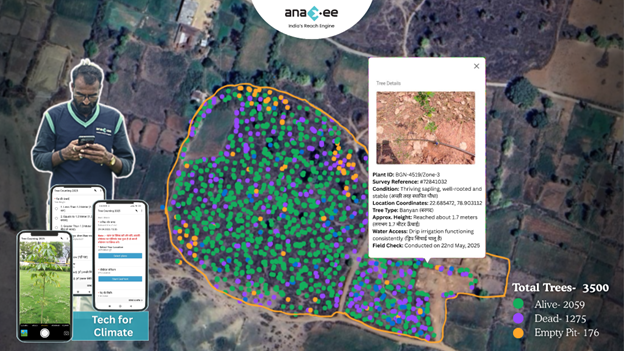
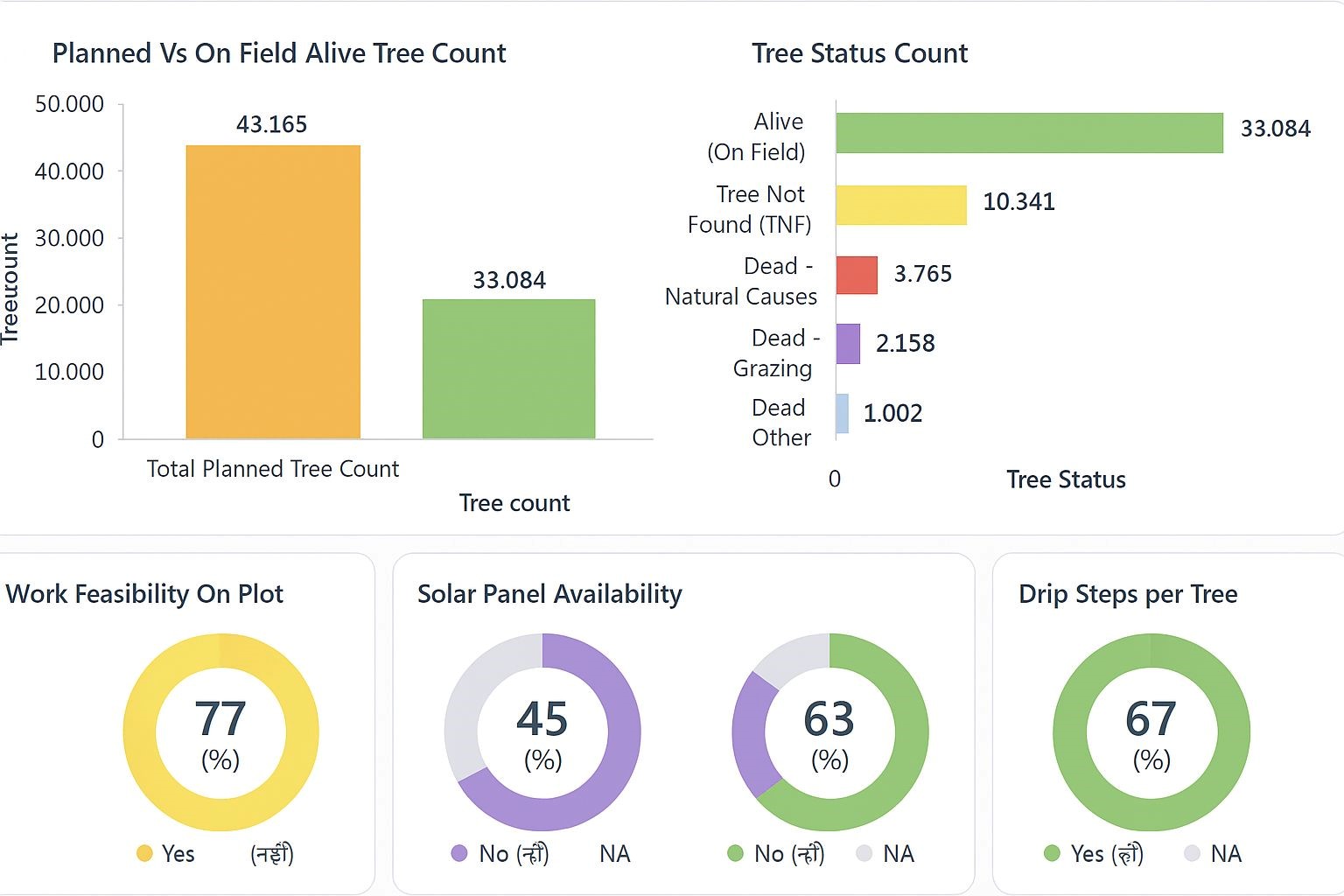
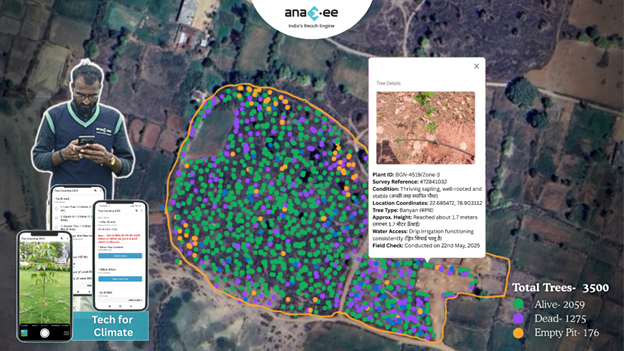
Madhya Pradesh’s 2023 Forest Report Card:
1. How Green Is the “Heart of India” in 2023?
- Total Forest Cover: 77,073 km²- a quarter (≈ 25 %) of the state’s 308,252 km² landscape.
- Inside RFA vs Outside: 67,770 km² lies inside recorded forest area, while 9,303 km² sits on revenue & private lands.
- Canopy Classes: 7,021 km² Very Dense, 33,509 km² Moderately Dense, 36,543 km² Open Forest.
- Net Two‑Year Change (2021→2023): +417 km² VDF, –310 km² MDF, –134 km² OF inside RFA—showing densification in key blocks.
Takeaway: MP added dense green core even as some medium‑density tracts opened up—likely selective harvesting + rapid teak/sal regrowth.
2. Winners & Losers: District Signals
A quick scan of 52 districts shows mixed fortunes — Balaghat, Chhindwara and Betul hold >50 % forest cover, while Bhind and Datia remain below 10 %. Eastern districts (Sidhi, Singrauli) gained canopy after community teak protection, whereas western Malwa lost patch forests to soy expansion.
3. What’s Growing Where – Forest‑Type Mosaic
Dry deciduous formations dominate: Dry Teak (21,715 km², 27 %) and Southern Dry Mixed Deciduous (19,581 km², 24 %) head the list. Moist Sal pockets (~2,747 km²) in the east are critical climate refugia.
Why it matters: Teak builds commercial volume fast; Sal locks dense carbon but burns easily when litter dries—dual management needed.
4. Fire: The Elephant in the Sal Forest
Nearly 33 % of MP’s woods fall in “Highly” or worse fire‑prone bands; another 49 % is “Less fire prone” fileciteturn3file8. The 2024 heatwave pushed fire alerts above 18,000. Hotspots: Shahdol‑Umaria belt (Sal litter) and Ratapani‑Sehore teak ridges.
5. Species, Biomass & Carbon Treasure
| Segment | Top Species | Trees (‘000) | Volume (Mm³) |
| RFA | Tectona grandis | 348,017 | 62 |
| Shorea robusta | 153,943 | 62.2 | |
| Rural | Butea monosperma | 76,206 | 16.6 |
| Acacia nilotica | 47,313 | 9.9 | |
| Urban | Azadirachta indica | 1,758 | 1.25 |
These numbers translate to >450 Mt CO₂e stored—a prime pool for carbon credits if monitored right.

6. NTFP Economy – The Tendu & Mahua Story
- Tendu Leaves: 115 million trees of Diospyros melanoxylon—₹700 cr annual trade.
- Mahua & Sal Seed: 9 M trees offer $200 M untapped nutraceutical value.
Digital traceability could raise collector income by 30 % through direct buyer links.
7. The Invasion We Ignore
Lantana camara carpets 5,914 km²—more than Goa’s area—choking teak regeneration. Drones + community removal credits can flip this liability into livelihood.
8. Carbon & ESG Playbook for 2025–30
- Dense‑Patch Carbon Projects: Target 417 km² of new VDF for premium credits.
- Fire‑Resilient Buffer Belts: Neem + Bamboo rings around Sal stands—backed by Green Credit funding.
- Invasive‑to‑Bio‑char: Pay villages ₹1/kg lantana → pyrolyse → bio‑char into soy farms.
9. Action Checklist for Policy & CSR
| Priority | Action | Metric | Timeline |
| Fire | 100 community rapid squads | <5 min response | 2025 |
| Carbon | Register 50,000 ha teak‑sal REDD+ | 2 Mt CO₂e credits | 2026 |
| NTFP | E‑market for Tendu/Mahua | 30% farm‑gate price | 2024 |
Bottom line: Madhya Pradesh sits on a green goldmine- dense teak, carbon‑rich Sal and a people‑centric NTFP economy. Digitization is the accelerator. Let’s put the “heart” of India at the heart of climate action. To know more connect with sales@anaxee-wp-aug25-wordpress.dock.anaxee.com.