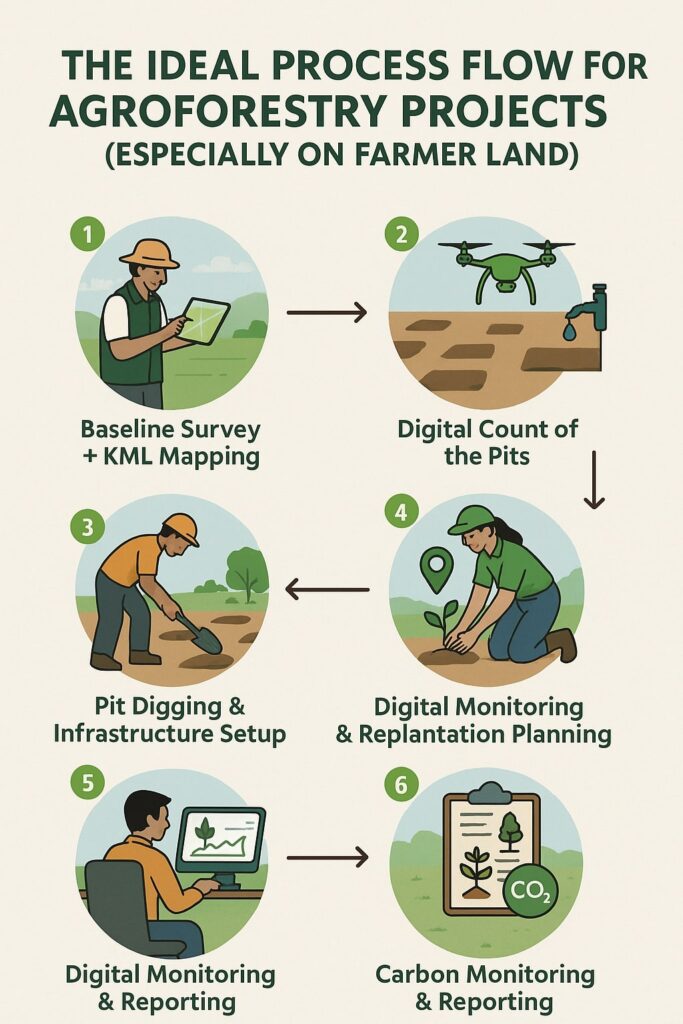
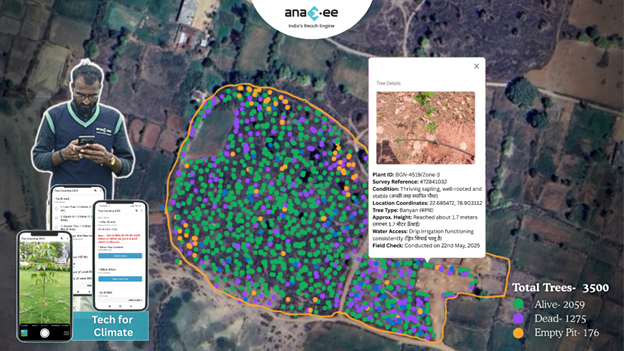
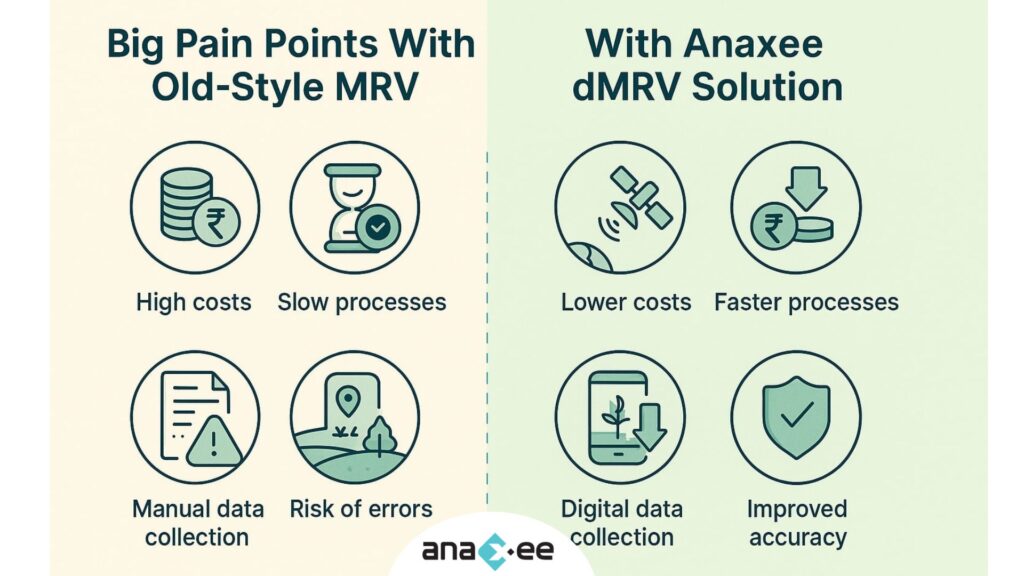
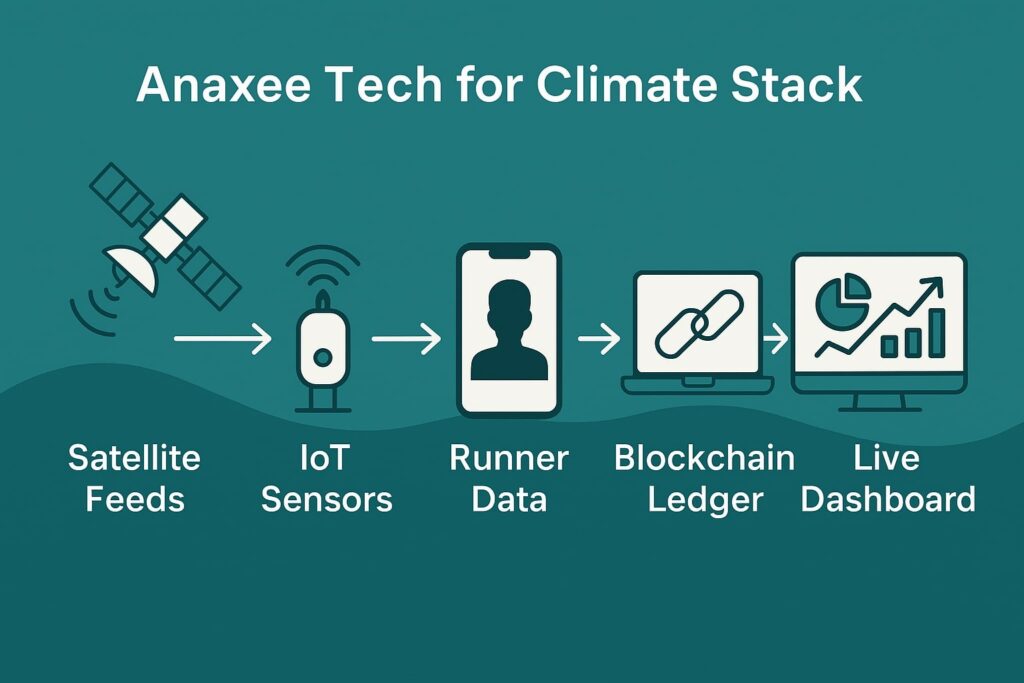
Biochar Projects in India: From Soil Health to Marketable Carbon Removals — A Practical, No-Nonsense Guide for Developers and Buyers
Biochar can be a credible carbon-removal pathway and an agronomic input — but only if projects confront three messy realities head-on: (1) feedstock sourcing that avoids diversion or indirect emissions, (2) pyrolysis process control that guarantees carbon stability, and (3) soil carbon measurement that is conservative, repeatable and auditable. Buyers love the headline — “permanent carbon in the soil” — but verifiers and scientists will ask for lab analyses, decay-model transparency, and careful baseline/additionality. If Anaxee designs biochar pilots around traceable feedstock chains, validated pyrolysis lab certificates, conservative permanence factors, rigorous soil sampling and transparent benefit sharing, the credits will survive scrutiny and command a premium. If you shortcut any of these, expect pushback, discounting or reputational cost.
1. Why biochar? The promise, and the necessary skepticism
Biochar sits at a rare intersection: it can improve soil health, reduce nutrient/runoff losses, and lock carbon in a form scientists generally agree is more stable than uncharred biomass. That’s the promise. The skepticism is equally real: not all biochar is equal. The climate value depends on feedstock, pyrolysis temperature, residence time, and what happens to the biomass if not turned into char.
Key questions you must treat honestly from day one:
-What would the feedstock have been used for otherwise? (baseline displacement)
-Does producing biochar create a carbon debt in the supply chain? (collection, transport, drying)
-How stable is the char in your soil and climate? (decay rates vary)
-Are the agronomic benefits genuine and durable, or context-specific short-term gains?
These are not academic quibbles. They determine whether your credits are durable, additional and marketable.
2. What a biochar carbon project actually sells
Put simply: a biochar project sells carbon sequestration in a pyrogenic form — the fraction of carbon in the produced char that remains stable in soil for climate-relevant timescales (decades to centuries). Unlike tree planting (where permanence risks center on fire, harvest, land-use change), biochar permanence is about chemical stability and soil processes. You must convert a mass of feedstock into an auditable quantity of stable carbon, and then show that the soil retains it over time according to a conservative model.
There are two revenue streams (often intertwined):
Carbon removals credits — the quantified, conservative estimate of long-term carbon sequestered in soil due to biochar application.
Co-benefits monetisation (optional) — agronomic yield, reduced fertilizer need, water retention, local livelihoods; useful for impact buyers but must be evidence-backed.
Never oversell both simultaneously without rigorous evidence. Buyers will discount if agronomic benefits are speculative.
3. Feedstock: the core integrity issue
Feedstock choice is political, environmental and commercial. A project’s integrity rises or falls on whether feedstock sourcing causes direct or indirect emissions, food/forage competition, or land-use change.
Practical rules:
-Prefer waste residues: agricultural residues, processing waste, or invasive biomass that would otherwise rot, be burned openly, or require disposal. But don’t assume “waste” is free of competing uses — fodder, bedding, or brick kilns sometimes use the same residues. Document local usage.
-Avoid virgin wood from standing trees: converting live trees to char is almost never additional or acceptable.
-Traceability is mandatory: each feedstock batch should have a documented origin, weight, moisture content at intake, and a chain-of-custody record. Build simple field receipts with GPS and countersigned notes.
-Calculate opportunity cost: what the biomass would have been used for absent the project (baseline) must be defensible. If a residue is typically burned as fuel, turning it into biochar shifts emissions; if it was used as animal bedding, the analysis must capture that trade-off.
Don’t assume local communities won’t push back if residual value is expropriated; include stakeholders early in the feedstock policy and benefit-sharing plan.
4. Pyrolysis technology: temperature, yield, and stability
Pyrolysis — heating biomass in low-oxygen conditions — produces biochar, gases and bio-oil. The key control variables for carbon projects are:
-Temperature and residence time: higher temperatures typically increase aromaticity and carbon stability but reduce char yield per ton of feedstock. There’s a trade-off between quantity of char and its long-term stability. Projects must declare their operating point and justify how that maps to stability parameters.
-Process type: slow pyrolysis tends to yield more char; fast pyrolysis prioritises bio-oil. For carbon projects, slow, controlled pyrolysis is usually preferred for higher char yields.
-Char characterization: lab tests are mandatory. Measure fixed carbon fraction, volatile matter, ash content, aromaticity indicators (e.g., H/C ratio), and specific surface area (if claimed). These metrics feed into the decay model used in the PDD.
Operational imperatives:
-Use certified pyrolysis units with documented operating logs (temperature, feed rate, residence time). Don’t rely on “we ran it at ~500°C” claims without continuous monitoring logs.
-Retain representative char samples per batch and archive them for auditing. Randomly test samples in third-party labs to prevent bias.
-If your process lacks instrumented controls and archived logs, VVBs will treat your ex-ante carbon estimates with extreme scepticism.
5. How much carbon is stable? Measurement, modelling, and conservative accounting
This is the hard technical core for MRV teams: transforming a ton of biomass feedstock into an auditable amount of stable soil carbon.
Basic steps:
Mass balance at the plant: measure dry mass of incoming feedstock and output char mass (all on dry mass basis). Keep moisture logs.
Char carbon content: determine fixed carbon fraction (%) by lab analysis. Multiply output char mass × carbon fraction to get char C mass.
Stability fraction: not all char C is permanent. Apply a conservative stability fraction (the share of char C expected to remain in soil after the relevant time horizon). That fraction must be justified with lab data and literature; use conservative estimates accepted by registries.
Soil residence and fate: account for application loss pathways (runoff, erosion, ploughing depth changes) and any subsequent soil processes that can mineralise a portion of char C.
Two pragmatic rules:
-Use conservative stability factors in ex-ante claims (registries and buyers prefer lower, defensible numbers that survive scrutiny).
-Present sensitivity analyses: show best-estimate and conservative scenarios; buyers appreciate transparency and will prefer the conservative baseline.
Remember: verifiers will ask for the raw lab files, instrument calibration certificates, and chain-of-custody for samples.
6. Soil carbon measurement: sampling design and statistical basics
Counting soil carbon is expensive and error-prone if done badly. But it’s the gold standard for demonstrating real sequestration in situ, especially if you seek to show net soil C increases beyond the char carbon you applied (e.g., priming effects).
Design principles:
-Baseline sampling: collect soil cores across representative strata (soil type, cropping system, topography) before any application. Record depth increments (e.g., 0–10 cm, 10–30 cm). Baseline is non-negotiable.
-Control plots: where feasible, use randomized control plots (no-biochar) to detect non-biochar drivers of change. This strengthens additionality claims.
-Sufficient replication: soil C is spatially variable — sample sizes must produce confidence intervals that meet verifier requirements. Plan statistically (not heuristically).
-Standardised lab methods: use dry-combustion CHN analyzers for organic C determination; report uncertainty, detection limits, and QA/QC logs. Use the same lab and method across monitoring cycles.
-Re-sampling cadence: re-sample at conservative intervals — e.g., 1 year, 3 years, 5 years, depending on the registry and decadal permanence expectations. Soil carbon accrues slowly; don’t promise large near-term gains based solely on yield improvements.
If you cannot afford comprehensive soil sampling, you can still sell removals based on feedstock → char mass accounting with conservative stability fractions — but expect lower unit prices. Direct soil measurements command higher confidence and price if done well.
7. Additionality, leakage and co-impacts: the accounting perimeter
Biochar projects must pass the same additionality and leakage tests as other carbon projects.
-Additionality: demonstrate the biochar activity would not have happened without carbon revenue. This is tricky when small-scale entrepreneurs or agronomic experiments could scale without carbon finance. Build a clear financial model showing the project is not economically viable without carbon income (e.g., capital for pyrolysis units, logistics, or farmer incentives).
-Leakage: could using residues for char divert them from alternative uses, forcing replacement biomass harvesting elsewhere? Estimate such indirect effects and, if material, apply leakage deductions or buffer credits. Document assumptions transparently.
-Non-GHG co-impacts: soils can benefit (yield, water retention) or sometimes suffer (if char contains contaminants or changes soil pH). Monitor for unexpected negative impacts and include them in your social and environmental safeguards.
Don’t rely on wishful thinking. Verifiers will probe the baseline counterfactual and whether the project creates displacement of existing resource uses.
8. MRV practicalities: what your verification folder must contain
If you want a VVB to pass on first review, prepare this folder — it’s not optional:
-Feedstock logs: batch receipts, GPS origin, supplier contracts, moisture analysis, and sample archives.
-Pyrolysis logs: continuous temperature-time profiles, feed rates, unit run IDs, representative char yields per run.
-Lab certificates: char fixed carbon %, volatile matter, ash content, H/C ratios, lab calibration certificates, and lab chain-of-custody forms.
-Soil sampling files: baseline and follow-up core sample IDs, GPS, depth logs, lab results, and QA/QC checks.
-Mass-balance spreadsheet: raw data with calculations from feedstock dry mass → char mass → char C → stable C with clearly shown formulas. Maintain version control and preserve raw files.
-Project governance & community consent: feedstock access agreements, benefit sharing, and grievance mechanism records.
-Model documentation: the decay model and literature justification for chosen stability fractions and any factors applied.
If any of these elements are missing or poorly documented, the VVB will increase uncertainty factors or reject claims.
9. Costs and economics: realistic budgeting
Biochar projects have predictable cost centers. Budgeting conservatively avoids painful write-downs later.
Typical cost categories:
-Capital: pyrolysis units (from small mobile kilns to fixed industrial units). Quality, instrumented units cost more but provide audit trails.
-Feedstock logistics: collection, drying, grinding, transport. Moisture reduction is often a hidden cost — wet feedstock lowers yield and increases energy needs.
-Lab testing: batch char characterization and soil sample analysis. These are recurring and non-trivial.
-Soil sampling & MRV: field teams, coring equipment, transport, and lab costs.
-Operations & management: local teams, data processing, inventory systems.
-Verification & registry fees: VVB cycles and registry issuance costs.
-Buffer and contingencies: for permanence risks, leakage or lower-than-expected stability.
Do not underprice MRV and lab testing. They are the marginal cost that determines whether credits survive validation.
10. Commercialization: who buys biochar credits and why
Buyer demand varies. Typical buyer types and their motivations:
-High-integrity removals buyers (tech firms, net-zero pledgers): they want conservative, well-documented removals they can confidently book against targets. They will pay a premium for verifiable soil carbon with rigorous MRV.
-Impact buyers: NGOs or corporates interested in soil health and livelihoods may buy projects with demonstrable co-benefits even if carbon prices are modest.
-Commoditised buyers: traders looking for volume may accept lower MRV rigour at a discount; these are riskier counterparties.
Packaging matters: deliver small digital dashboards with char mass flows, archived lab files, and anonymised soil result extracts to high-integrity buyers. They will ask for chain-of-custody and may request spot re-tests.
11. Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
Be direct: many projects fail on avoidable errors. Avoid these:
-Weak chain-of-custody: failing to document feedstock origin exposes you to leakage accusations. Fix: standard receipts + GPS + supplier contracts.
-Poor pyrolysis controls: hand-built kilns without logs make stability claims impossible to justify. Fix: instrumented units and archived run logs.
-Insufficient soil sampling: tiny sample sizes produce wide confidence intervals and unreliable claims. Fix: consult a statistician and build a representative sampling frame.
-Over-claiming co-benefits: yield improvements are context-dependent; don’t promise what you can’t prove. Fix: conservative claims and pilot data.
-Ignoring community impacts: feedstock extraction can create local grievances if not consented and compensated. Fix: explicit benefit sharing and FPIC where applicable.
Shortcuts increase audit friction and ultimately lower project value.
12. Project design template — from pilot to program

Here is a practical stepwise blueprint Anaxee can replicate.
Phase 0 — Feasibility & stakeholder scan
-Map feedstock availability, current uses, and competing markets.
-Test community sentiment on feedstock use and land rights.
-Conduct an initial LCA scoping to identify high-risk upstream emissions.
Phase 1 — Pilot (replicable, data-centric)
-Install a pilot pyrolysis unit with full instrumentation.
-Produce char at controlled settings; archive samples.
-Run a small soil sampling regime (pilot control vs treated plots).
-Measure agronomic outcomes and perform preliminary farmer interviews.
-Build mass-balance spreadsheets and model stability fractions conservatively.
Phase 2 — Scale (standardise and govern)
-Standardise feedstock receipts and supplier contracts.
-Deploy certified pyrolysis units and train operators.
-Implement a central MRV hub for data ingestion, char archiving, and soil sample management.
-Create a benefit-sharing mechanism linking feedstock suppliers and smallholders to revenue streams (not just promises).
-Engage VVB early with pilot data to align monitoring expectations.
Phase 3 — Program & commercialization
-Aggregate across sites, harmonise PDD documentation and governance.
-Prepare buyer packages (conservative ex-ante claims + soil re-sampling schedule + QA documents).
-Price credits transparently accounting for buffer pools for risk.
13. PDD & MRV language: audit-ready clauses
Objective (sample):
“Quantify the amount of pyrogenic carbon sequestered in agricultural soils through application of conventionally produced biochar, using a conservative, auditable mass-balance approach (feedstock dry mass → char mass → char C → stable C) complemented by soil sampling for a subset of plots. All laboratory certificates, plant run logs, and chain-of-custody documentation will be retained in the project MRV repository and made available to the VVB.”
Monitoring approach (sample):
“Mass flow monitoring will record dry feedstock intake, char output mass, and batchwise char sampling for laboratory determination of fixed carbon. Soil cores from stratified representative plots (treatment and control) will be collected at baseline, Year 1, Year 3 and Year 5 and analysed using dry combustion. Ex-ante stable fraction assumptions will be conservative and justified with third-party lab tests and literature.”
Use these as starting points and make your numbers conservative.
14. Anaxee’s competitive playbook — where you must get ruthless

Anaxee’s strengths (local teams, dMRV, last-mile execution) can make biochar commercially viable — but execution must be ruthless about documentation.
Concrete moves:
Invest in one well-instrumented pilot: purchase a quality slow-pyrolysis unit with data logging; get char samples tested in reputable labs. This single pilot will define your PDD parameters.
Standardise receipts and digitalise the supply chain: use simple mobile forms for supplier receipts with GPS and photos to create tamper-resistant evidence.
Build a central MRV hub: ingest run logs, lab files, soil data and generate audit packs automatically. This reduces VVB time and fees.
Offer a transparent benefit-share to suppliers: a fair, quick payment mechanism prevents grievances and secures feedstock.
Pitch conservative credits to high-integrity buyers first: premium buyers will help establish price anchors.
Don’t try to be everything at once. Do one well-documented project, prove the model, then scale.
15. Hypothetical case study: a replicable pilot model
Context: Agro-processing clusters producing cassava/peanut shells in two districts, residues currently burned or left to rot.
Pilot size: 3,000 t/year feedstock capacity; expected char yield 15% dry mass.
Key controls: instrumented slow-pyrolysis unit, char batch archiving, lab char characterization, baseline soil sampling on 100 farm plots (50 control, 50 treatment).
Economics: feedstock payments to suppliers, capex amortised over 7 years, MRV and lab testing funded by early carbon forward sales at conservative price.
Risk mitigation: buffer pool allocation (5–10%), supplier contracts with grievance redress, drying yards to reduce moisture costs.
Outcome: conservative ex-ante carbon claim based on char mass × fixed C × conservative stability fraction; soil sampling used to validate and, over time, potentially increase confidence intervals and raise crediting volumes.
16. Buyer due diligence checklist (what buyers will ask)
Buyers who pay for removals will insist on:
-Mass-balance spreadsheet with raw feedstock & char logs.
-Laboratory certificates for char and soil analyses (with QA/QC).
-Chain-of-custody receipts for feedstock with GPS evidence.
-Pyrolysis run logs (temperature/time).
-Baseline, control plots, and soil sampling plan showing statistical adequacy.
-Evidence of supply-chain consent and benefit sharing.
If you can’t produce these in the first 72 hours, you will struggle to close quality buyers.
17. Ethics, community and co-benefits — don’t treat them as marketing copy
Biochar projects intersect livelihoods. If you extract biomass from smallholders without fair compensation, or if you promote feedstock diversion from animal bedding to char, you erode trust and create perverse outcomes. Document how suppliers are chosen, paid, and how their livelihoods are protected.
Co-benefits must be proven:
-Measure yield changes with randomized or matched control plots.
-Test soil health indicators (Cation Exchange Capacity, pH, available nutrients) for plausible agronomic claims.
-Be transparent about where biochar worked and where it didn’t — buyers appreciate honest reporting.
18. Final reality check — be conservative and transparent
Biochar is attractive. But the market will reward projects that are disciplined and transparent, not those that promise untested miracles. The correct posture is humility: treat ex-ante estimates as conservative hypotheses backed by lab and pilot data, not marketing copy. Buyers and verifiers will respect conservatism and clear audit trails.
If Anaxee wants to lead in biochar:
-Start with one instrumented pilot.
-Build standardised digital receipts and a central MRV hub.
-Use conservative stability fractions and publish sensitivity analyses.
-Prioritise feedstock traceability and supplier fairness.
-Engage a reputable VVB early with pilot data to align expectations.
Biochar can be both an effective soil amendment and a credible removal pathway — but only when the proofs are in the data, and that data is auditable.