How Indian Corporates are Using CSR to Drive Climate Action—and What’s Missing
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in India is no longer about one-off charity drives or building local infrastructure. Increasingly, corporates are realizing that their CSR budgets can become powerful tools for climate action. From reforestation and renewable energy to waste management and carbon projects, the shift is happening. But while the intent is clear, the missing link is transparency and accountability—something that current CSR approaches often overlook.
The CSR Landscape in India 
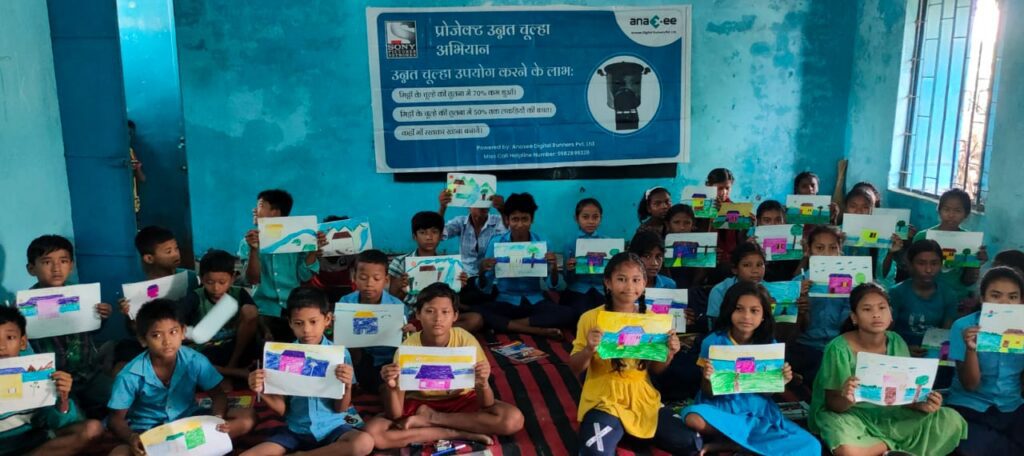
When CSR spending became mandatory in 2014 under the Companies Act, Indian corporates scrambled to comply. Initial projects were largely focused on education, health, or welfare—important, but short-term. Over the past decade, however, there’s been a clear pivot toward sustainability and climate-focused CSR. Some key trends: -Tree planting drives have expanded into large-scale agroforestry and reforestation initiatives. -Renewable energy CSR supports solar electrification of rural schools and communities. -Waste management and circular economy initiatives are now core CSR programs. -Carbon offset-linked projects are slowly entering the mainstream. Big players like Tata, Mahindra, Reliance, and Infosys have all integrated sustainability into CSR spending. Yet, despite these advances, CSR is often still treated as a PR exercise rather than a structured, long-term climate strategy.
Why Climate Projects Attract CSR Funding 
Climate projects are attractive to corporates for three reasons:
- Alignment with ESG Goals: CSR funds directed into climate align with broader Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks that investors and regulators demand.
- Dual Impact: A climate project delivers both environmental benefits (carbon sequestration, biodiversity, resilience) and community benefits (livelihoods, health, awareness).
- Reputation Management: Climate-linked CSR makes headlines, builds brand equity, and signals responsibility to shareholders and the public.
In other words, climate projects allow corporates to demonstrate purpose while staying competitive.
Case Examples of CSR in Climate
- Tata Group: Runs extensive reforestation and watershed management projects under CSR, often tied to local communities and livelihood programs.
- Mahindra & Mahindra: Launched the “Hariyali” tree plantation initiative, aiming to plant millions of trees with community involvement.
- ITC: Integrated CSR with sustainability goals by combining social forestry, water stewardship, and carbon projects.
- Infosys: Invested in renewable energy CSR projects, particularly solar electrification for rural schools.
These examples showcase ambition. But the real question is: Are these projects transparent and measurable at the level of carbon markets? Often, the answer is no.
What’s Missing in CSR Climate Action 
Despite progress, CSR-driven climate projects in India often share common problems: -Short-Term Orientation: Many projects are structured for 2–3 years, while climate impact requires 15–20 year commitments. -Data Gaps: Monitoring and verification are either absent or limited to photographs and reports, with little scientific rigor. -Overreliance on NGOs: While NGOs play a vital role, corporates often hand over entire CSR projects to NGOs without empowering them with tech, roadmaps, or market linkages. -Lack of Carbon Accounting: Most CSR projects don’t track carbon sequestration or emission reductions in line with international standards. This creates a paradox: CSR funds are spent, communities are engaged, trees are planted—but long-term transparency and accountability remain missing.
The Role of Empowering NGOs
Corporates cannot sidestep NGOs—they are critical intermediaries between companies and communities. But NGOs are not equipped to ensure climate integrity alone. They need: -Technology Platforms: For real-time monitoring and reporting. -Training in Carbon Methodologies: To align community projects with Verra, Gold Standard, or national frameworks. -Long-Term Roadmaps: That outlast short project cycles. -Implementation Partners: To bridge the gap between corporate funding and grassroots execution. Without empowerment, NGOs become weak links in CSR climate projects. With empowerment, they become engines of trust and efficiency.
How Anaxee Brings Transparency to CSR Climate Action
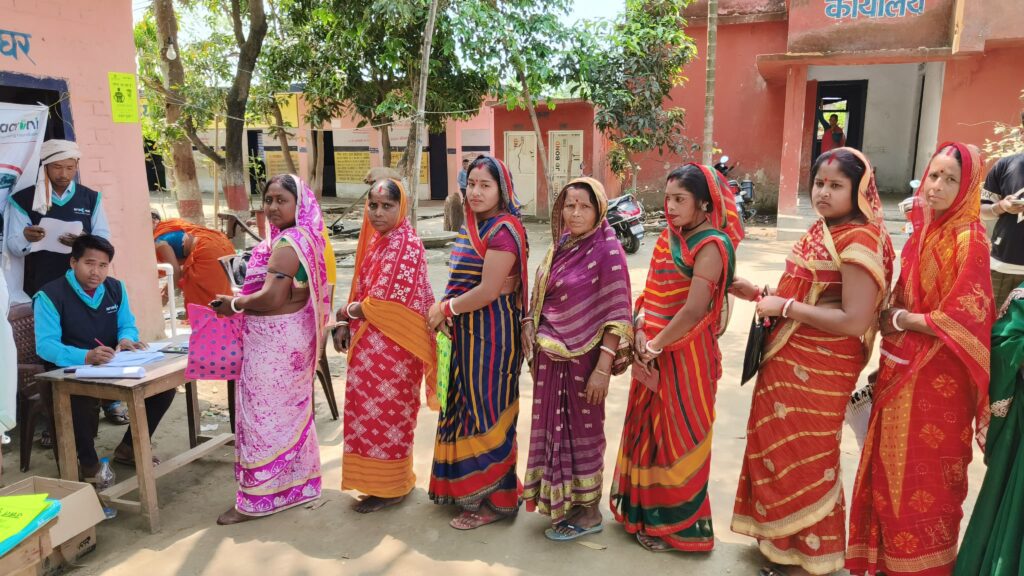
At Anaxee, we specialize in addressing these gaps: -Last-Mile Data Collection: Through our 40,000+ Digital Runners, we ensure on-ground verification across rural India. -dMRV Tools: Our digital monitoring, reporting, and verification systems provide corporates with transparent dashboards. -NGO Empowerment: We integrate NGOs into our tech-driven framework so they can scale beyond traditional limits. -Carbon Project Alignment: Projects are structured for 15–20 years, ensuring they are creditable, verifiable, and impactful. This combination ensures CSR money isn’t just spent—it creates measurable climate outcomes.
Looking Ahead: CSR’s Future in Climate Action
The trajectory is clear: Indian corporates will continue channeling more CSR funds into climate projects. But without transparency, integrity, and long-term structures, much of that money risks being underutilized. The future of CSR climate action in India will depend on three things:
- Corporate Commitment to long-term climate strategies.
- Empowered NGOs embedded into transparent systems.
- Implementation Partners like Anaxee ensuring measurable results.
Key Takeaways for Corporates
-Climate-focused CSR is not just compliance—it’s strategic. -Short-term impact is not enough. CSR projects must be designed for decades, not years. -NGOs are necessary but not sufficient—they must be empowered. -Transparent implementation partners like Anaxee are essential for credibility. Because in the end, CSR in climate is not about planting trees for the photo-op. It’s about building trust, ensuring transparency, and delivering measurable climate impact.
About Anaxee: Anaxee drives large-scale, country-wide Climate and Carbon Credit projects across India. We specialize in Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) and community-driven initiatives, providing the technology and on-ground network needed to execute, monitor, and ensure transparency in projects like agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, improved cookstoves, solar devices, water filters and more. Our systems are designed to maintain integrity and verifiable impact in carbon methodologies.
Beyond climate, Anaxee is India’s Reach Engine- building the nation’s largest last-mile outreach network of 100,000 Digital Runners (shared, tech-enabled field force). We help corporates, agri-focused companies, and social organizations scale to rural and semi-urban India by executing projects in 26 states, 540+ districts, and 11,000+ pin codes, ensuring both scale and 100% transparency in last-mile operations. Connect with Anaxee at sales@anaxee.com