India’s Article 6.2 Breakthrough: Japan Partnership and Eligible Activities for Global Carbon Trading
For years, the carbon market in India has been described as “promising” but not yet fully functional. That changed in August 2025, when India signed its first Memorandum of Cooperation (MoC) under Article 6.2 of the Paris Agreement with Japan.
This moment marks a turning point: India’s entry into official international carbon trading.
And here’s what makes it even more significant: just a month earlier, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) had already published a list of eligible activities under Article 6.2 (July 14, 2025 memorandum). That means developers, corporates, and investors know exactly which sectors and technologies can generate credits under this framework.
Together, these two steps—the Japan partnership and the activity list—set the foundation for India’s global carbon market era.
In this detailed article, let’s break it down: what Article 6.2 is, what the India–Japan partnership means, which activities qualify, how the money flows, and why this is such a historic opportunity.
🌍 What Exactly is Article 6.2?
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, created frameworks for countries to cooperate in achieving emission reduction targets. Article 6 is the part that deals with international cooperation and carbon markets.
-Article 6.2 enables bilateral or multilateral trading of emission reductions between countries.
-A country can invest in emission reduction projects in another country and claim the credits towards its own Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
-These internationally traded units are known as Internationally Transferred Mitigation Outcomes (ITMOs).
Unlike voluntary carbon markets, Article 6.2 is government-backed and NDC-aligned. That makes it more credible, and more attractive for large-scale investments.
For India, this isn’t just climate diplomacy. It’s a way to bring in foreign investment, technology transfer, and long-term partnerships while strengthening its Net Zero 2070 pathway.
🇮🇳🤝🇯🇵 The India–Japan Joint Crediting Mechanism
On August 29, 2025, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) announced the signing of an MoC with Japan on the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM).
Why is this so important?
First Agreement under Article 6.2: India is no longer on the sidelines. It’s officially part of international carbon credit trading.
Technology Transfer: Japan is a leader in advanced low-carbon technologies, from hydrogen to energy efficiency. These can now flow into India.
Investment Flow: Projects in India that were financially unviable can now get foreign backing.
Capacity Building: It’s not just about money—JCM includes training, knowledge exchange, and systems for better project monitoring.
High-Level Political Will: With both PM Narendra Modi and PM Shigeru Ishiba highlighting the partnership, this is top-tier diplomacy.
The message is clear: India is open for global carbon business.
📜 The July 2025 Memorandum: Eligible Activities Under Article 6.2
The real game-changer is the clarity provided by MoEFCC’s memorandum (July 14, 2025).
Instead of vague promises, the Government listed specific activities that will qualify for trading under Article 6.2. This removes uncertainty and signals where opportunities lie.
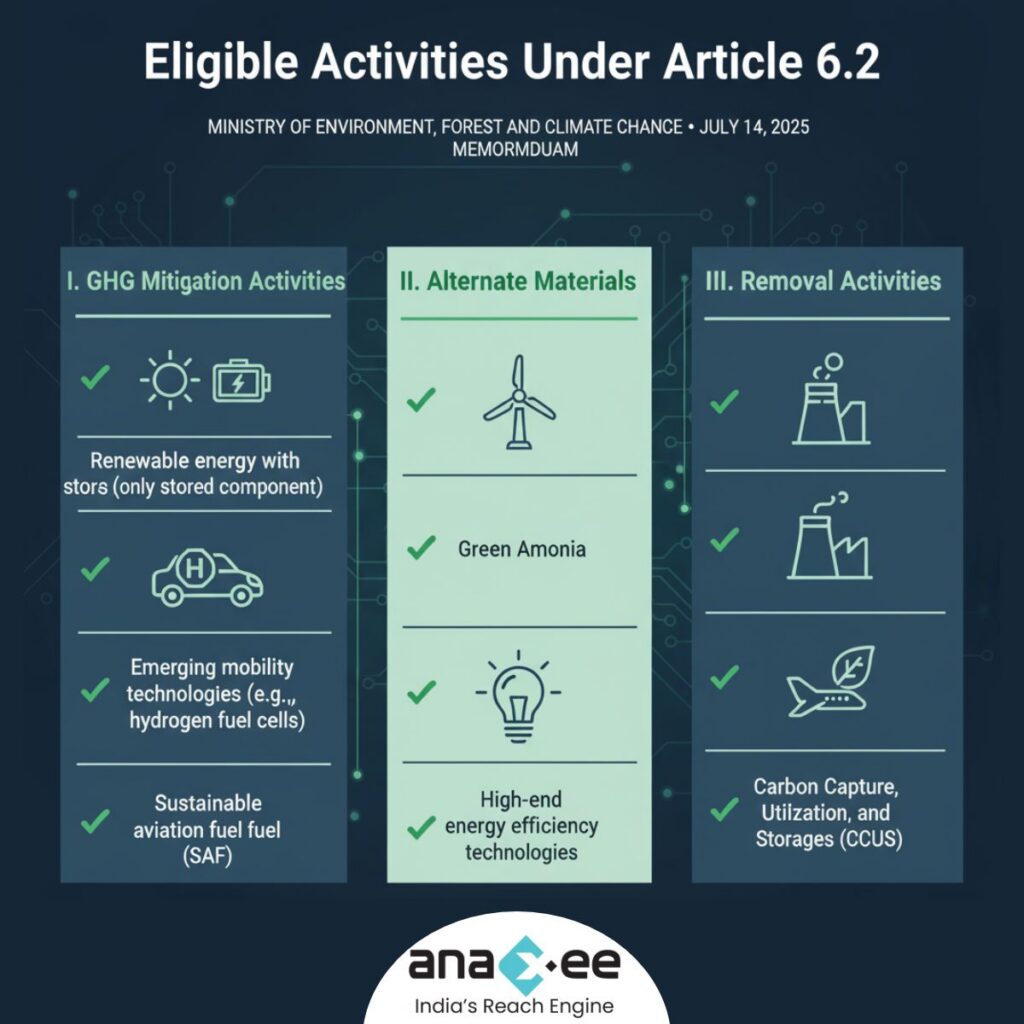
✅ I. GHG Mitigation Activities
-Renewable energy with storage (only the stored component)
-Solar thermal power plants
-Offshore wind projects
-Green hydrogen production
-Compressed bio-gas projects
-Emerging mobility technologies (e.g., hydrogen fuel cells)
-High-end energy efficiency technologies
-Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF)
-Best available industrial technologies for hard-to-abate sectors
-Ocean energy (thermal, tidal, wave, current)
-High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission for renewable integration
✅ II. Alternate Materials
-Green Ammonia
✅ III. Removal Activities
-Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
This list is valid for three years, after which NDAIAPA (the National Designated Authority for Implementation of the Paris Agreement) may update or revise it.
For businesses, this means one thing: certainty. You know what qualifies, so you can design projects and strategies accordingly.
💰 How the Money Will Flow
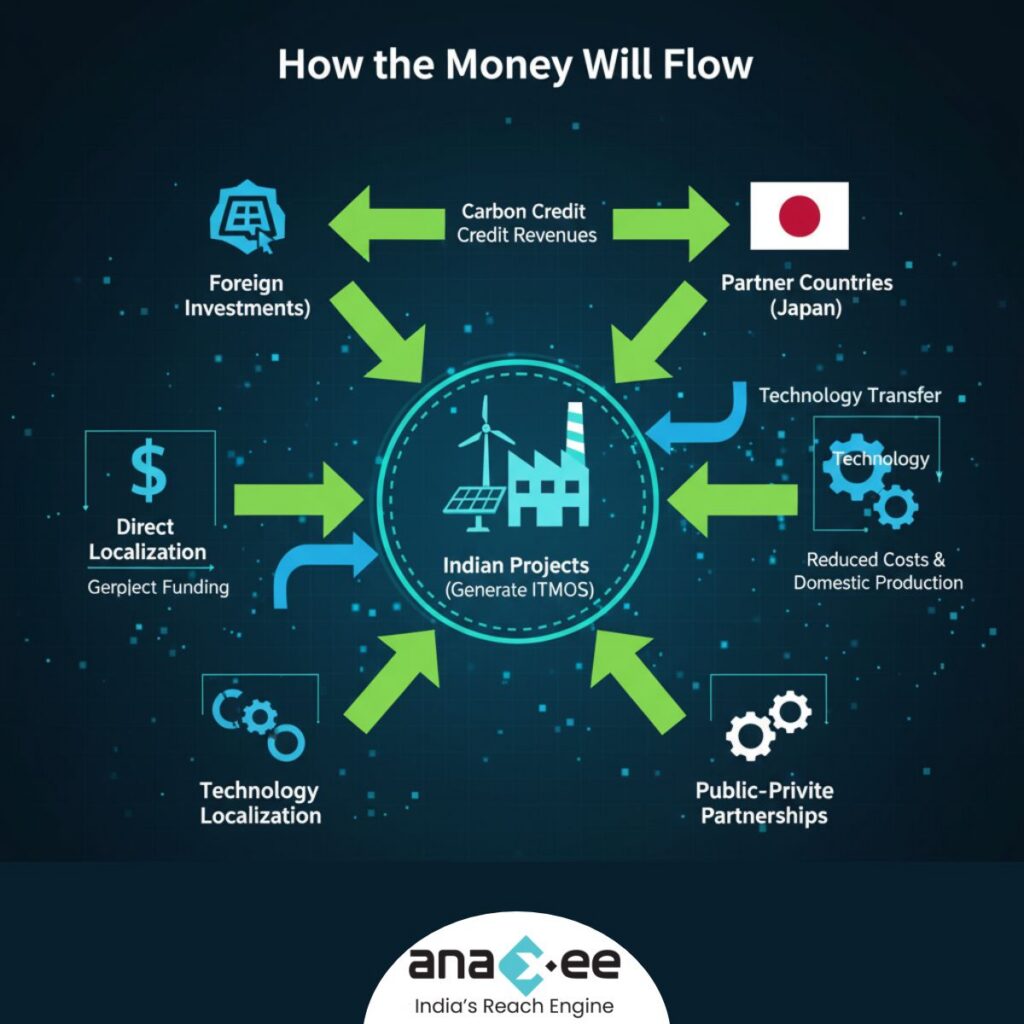
Article 6.2 opens multiple financial channels:
-Carbon Credit Revenues – Indian projects generate ITMOs, which partner countries purchase.
-Foreign Investments – International capital enters Indian projects directly.
-Technology Localization – With new technologies entering, domestic production scales up and costs fall.
-Public–Private Partnerships – Especially in aviation, industry, and energy storage, partnerships will accelerate.
Example: An Indian project producing sustainable aviation fuel can attract Japanese investment, cut airline emissions, and generate credits Japan counts toward its NDC. That’s triple value—finance, decarbonization, and market creation.
📈 Why This Is a Huge Opportunity for India
Global Carbon Market Access: India joins a $100+ billion international market.
Diverse Sectoral Benefits: Aviation, industry, energy, transport—all benefit.
Net Zero Finance: Helps fund India’s Net Zero 2070 commitments.
Global Credibility: Positions India as a climate market leader.
Future Agreements: Cabinet approval means MoEFCC can replicate the Japan deal with Europe, ASEAN, and others.
This is not incremental. This is transformative.
🏭 Sectoral Breakdown: Who Gains What?
-Renewables: Storage-linked solar, hybrid, and offshore wind projects are now directly eligible.
-Industry: Best available technologies and CCUS create space for heavy emitters to decarbonize profitably.
-Mobility: Fuel cells and EV-related solutions gain international backing.
-Aviation: With SAF listed, airlines finally have a credible finance mechanism for decarbonization.
-Agriculture & Energy: Compressed bio-gas projects link rural development with global carbon finance.
-Chemicals & Fertilizers: Green ammonia becomes a new frontier.
🏛️ Institutional Ecosystem
The MoEFCC leads implementation, supported by NDAIAPA. The July memorandum was circulated across ministries—Power, Mines, Heavy Industries, Aviation, Rural Development, MSME, and more—showing that Article 6.2 is not siloed.
It’s a whole-of-government strategy. Climate policy meets industrial policy meets foreign policy.
🌐 India’s Global Position
By operationalizing Article 6.2, India:
-Strengthens Indo-Japan ties.
-Positions itself for future deals with EU, ASEAN, and Middle East.
-Sets an example for other developing nations.
This is both an economic opportunity and a diplomatic lever.
⚠️ Challenges to Watch
-Governance Complexity: Multiple ministries and NDAIAPA approvals may slow progress.
-MRV Systems: Strong monitoring and reporting needed for credibility.
-Balancing Export vs. NDC Needs: Credits sold abroad must not undermine India’s commitments.
-High Costs: Some technologies, like CCUS, still face commercial barriers.
But with digital MRV tools, blended finance, and clear rules, these challenges can be overcome.
💡 Role of Private Players
This is where companies like Anaxee can make a difference.
-Project Developers: Can design projects aligned with eligible activities.
-Corporates: Can invest in Article 6.2 projects to offset or diversify.
-Investors: Can treat ITMOs as a credible, government-backed asset class.
Private innovation, last-mile execution, and digital MRV are critical for scaling.
🚀 From Japan to the World
The Japan MoC is only the first chapter. Next could be:
-Europe (offshore wind, CCUS)
-ASEAN (mobility and renewables)
-Middle East (green hydrogen partnerships)
India has Cabinet approval to sign more such MoCs. Each one expands the market.
📝 Conclusion: India’s Carbon Market at a Turning Point
Article 6.2 has finally moved from negotiation rooms to reality.
For India, it means:
-First operational MoC with Japan under JCM.
-Clear activity list for eligible projects.
-Finance + technology flows into priority sectors.
-Credibility and leadership in global climate markets.
This is not the time to stand back and observe. The rules are set, the framework is active, and the opportunities are real.
For developers, corporates, and investors: the Indian carbon market is open for business.
About Anaxee:
Anaxee drives large-scale, country-wide Climate and Carbon Credit projects across India. We specialize in Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) and community-driven initiatives, providing the technology and on-ground network needed to execute, monitor, and ensure transparency in projects like agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, improved cookstoves, solar devices, water filters and more. Our systems are designed to maintain integrity and verifiable impact in carbon methodologies.
Beyond climate, Anaxee is India’s Reach Engine- building the nation’s largest last-mile outreach network of 100,000 Digital Runners (shared, tech-enabled field force). We help corporates, agri-focused companies, and social organizations scale to rural and semi-urban India by executing projects in 26 states, 540+ districts, and 11,000+ pin codes, ensuring both scale and 100% transparency in last-mile operations. Connect with Anaxee at sales@anaxee.com