Carbon Pricing in India: Decoding the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS) and What It Means for Business
1. Why Carbon Pricing and Why Now?
India’s climate targets have teeth only if the cost of emitting carbon shows up on a CFO’s balance sheet. That is the simple logic behind carbon pricing—a policy tool that forces emitters to internalise the social cost of greenhouse‑gas (GHG) pollution. New Delhi is no stranger to market‑based regulation (think PAT, RECs), but 2025 is different. We now have a formal rate‑based Emissions Trading System (ETS) embedded in the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, 2023–24 (CCTS), backed by amendments to the Energy Conservation Act.
In other words, India is putting a price on carbon intensity rather than absolute tonnes. The shift is subtle but game‑changing for a fast‑growing economy that still needs to expand energy supply.

2. India in the Global Carbon‑Pricing League
According to the World Bank’s “State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2025”, India now sits in the same emerging‑economy cohort as Brazil, China, and Türkiye when it comes to regulated carbon markets.
– Coverage: Nine energy‑intensive sectors at launch—power, iron & steel, cement, aluminium, fertiliser, pulp & paper, petro‑refining, chemicals and textiles.
– Instrument: Rate‑based ETS + domestic voluntary offset window.
– Benchmark: Emission‑intensity targets, not a hard cap.
– Timing: Compliance cycle expected FY 2025‑26; voluntary methodologies approved March 2025.
Is this ambitious enough? Maybe not. But it’s a pragmatic design for an economy where absolute caps could stifle growth.
3. A Quick History of India’s Carbon‑Pricing Instruments
| Instrument | Year | How It Prices Carbon | Status & Lessons |
| Clean Energy Cess (Coal Cess) | 2010 → Rs 50/t; hiked to Rs 400/t by 2016 | Implicit carbon tax on coal | Generates >₹50,000 cr annually for clean‑energy fund, but industry calls it distortionary. |
| Perform, Achieve & Trade (PAT) | 2012 | Tradable energy‑saving certificates vs sectoral baselines | Reduced energy intensity 15‑25% in covered sectors; informs ETS design. |
| Renewable Energy Certificates (REC) | 2011 | Certificate market for clean kWh | Helped build 100 GW+ RE but faced price volatility. |
| CCTS (Rate‑based ETS) | 2023 | Tradable carbon‑credit certificates (CCCs) vs intensity benchmarks | Regulatory framework in force; compliance manual published Nov 2023. |
What sticks out?
- Tax vs Trade: India leaned on an implicit coal tax while the EU went cap‑and‑trade.
- Intensity, not Caps: Every scheme is benchmarked to intensity—consistent with a developing economy narrative.
- Administrative Lean: BEE is the common operator, so institutional memory transfers over.
4. The Legal Backbone: Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022
This amendment gave the central government explicit power to issue, trade, and retire carbon‑credit certificates. It also created statutory room for voluntary credits—a carve‑out many exporters wanted as CBAM pressure rose.
Key Provisions:
-Section 14A: Authorises central registry for carbon certificates.
-Section 58: Empowers BEE as market administrator.
-Penalty Clause: Non‑compliance fines up to two times market price of CCCs—enough to make CFOs sweat.
5. Anatomy of the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS)
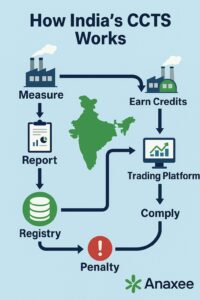
5.1 Compliance Mechanism
-Obligated entities must meet annual emission‑intensity targets.
-Over‑achievers receive Carbon Credit Certificates (CCCs); under‑performers must buy them or pay a penalty.
-MRV protocol follows ISO 14064 and IPCC 2006 guidelines.
5.2 Offset Mechanism (Domestic Voluntary Market)
Eight approved methodologies (renewables, green hydrogen, energy efficiency, mangrove AR, etc.) allow non‑ETS players to generate credits. Credits can be sold into the compliance market or to corporates chasing net‑zero pledges.
5.3 Registry & Trading Platform
An electronic trading platform is being built on power‑exchange infrastructure (IEX/PXIL) to avoid reinventing the wheel. Settlement cycle mirrors India’s short‑term power market (T + 1).
6. Rate‑Based ETS vs Cap‑Based ETS: A Critical Look
| Question | Rate‑Based ETS (India) | Cap‑Based ETS (EU) |
| Growth Flexibility | High – intensity target lets total emissions rise if GDP soars. | Low – absolute cap is fixed. |
| Environmental Certainty | Medium – depends on GDP, energy mix. | High – tonnes are fixed. |
| Data Requirement | Needs robust output data + emission factors. |
Needs accurate absolute emissions data.
|
| Competitiveness Shield | Better for export sectors; avoids immediate carbon leakage risk. | Exposed, leading to CBAM on imports. |
The trade‑off is clear: India opts for economic flexibility over guaranteed tonnage reductions. That choice invites scrutiny from trading partners—hence the CBAM threat.
7. CBAM: The External Price Tag India Can’t Ignore
The EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism enters its financial phase in January 2026. Analysts estimate Indian steel exporters could face ₹19,000 cr in CBAM charges by 2030 unless they decarbonise.
Negotiators are scrambling to protect exports, but the simplest antidote is a robust domestic carbon‑pricing system that proves “equivalent effort.” India’s shift from coal cess to CCTS is partly a CBAM‑defence strategy.
8. Sector‑by‑Sector Readiness
| Sector | Baseline Intensity (tCO₂e/unit) | Decarbonisation Levers | CCTS Implication |
| Power | ~0.8 tCO₂e/MWh | RE expansion, coal plant retrofits | Likely to supply low‑cost CCCs in early rounds. |
| Steel | 2.2 tCO₂e/tcs | Green hydrogen, scrap‑EAF, CCS | High demand for CCCs; CBAM‑exposed. |
| Cement | 0.6 tCO₂e/t | Clinker‑factor cuts, AFR, waste‑heat recovery | Moderate deficit; cross‑link with PAT Phase VII. |
| Aluminium | 13 MWh/t electricity | Inert‑anode tech, renewable smelter |
Hurt by coal cess; needs CCTS credits until grid cleans up.
|
9. Numbers That Matter
-Coal Cess Pool: ~₹54,000 cr collected (FY 2010‑25). Little of it has flowed to climate projects—an efficiency gap CCTS aims to fix.
-Potential Market Size: BEE projects CCC demand at 180 MtCO₂e by 2030—roughly a ₹45,000‑crore annual market assuming ₹250/t average price.
-Voluntary Credits Pipeline: 8 approved methodologies could unlock 50 MtCO₂e offsets annually by end‑decade.
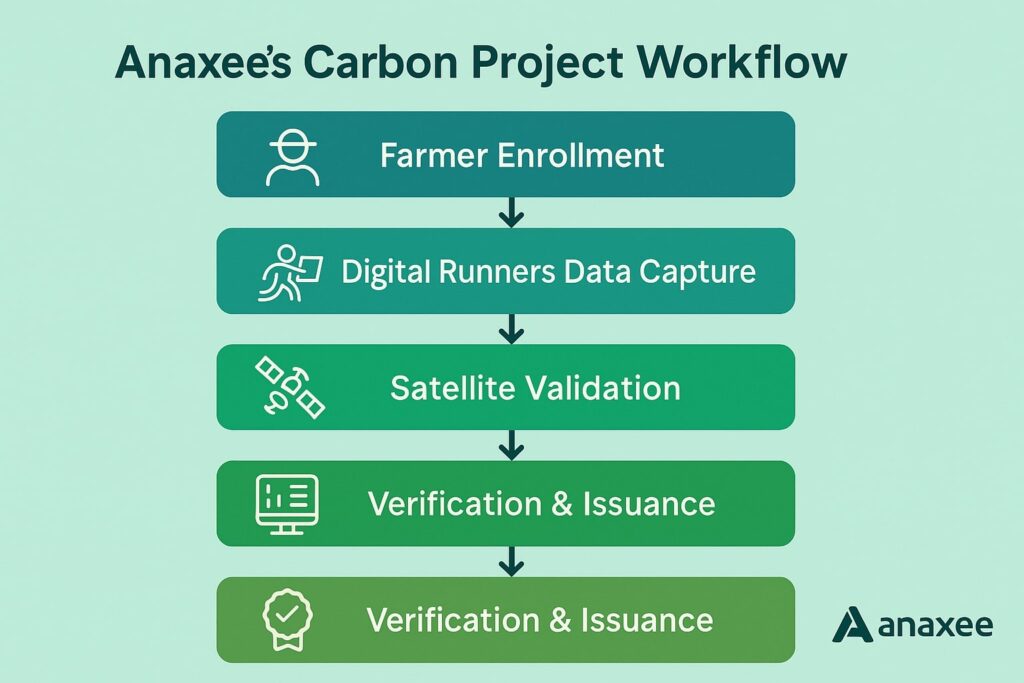
10. The Data & MRV Challenge—And Why Tech Players Like Anaxee Matter
Carbon pricing lives or dies on Measurement, Reporting & Verification (MRV). India’s grid is patchy with emission‑factor data, and many mid‑tier plants lack automated monitoring.
Where Anaxee fits:
- Last‑Mile Data Collection: With runners in 26,000+ villages, field‑level energy audits and biomass assessments feed verifiable project data into the registry.
- Digital MRV (dMRV): Mobile‑first data capture plus blockchain‑anchored audit trails reduce double‑counting risk—critical for credit quality.
- Community Projects: CCTS offset window covers mangroves, clean cooking, agro‑forestry. Anaxee’s rural network accelerates baseline surveys and credit issuance.
Bottom line: Carbon pricing is as strong as its data plumbing; that plumbing is a tech and outreach problem more than a policy one.
11. Pain Points No One Should Ignore
- Price Volatility: Without a price collar, CCCs could swing like RECs did in 2016.
- Registry Interoperability: Alignment with international standards (ICVCM, VCMI) is still work‑in‑progress.
- Delayed Penalties: Collection of non‑compliance fines historically lags in India’s power market—watch this space.
- Equity Concerns: SMEs outside top nine sectors risk being left behind unless voluntary credit pathways become affordable.
12. What Indian Corporates Should Do in the Next 12 Months
| Timeline | Action Items |
| Q3 2025 |
Map plant‑level emission intensity vs draft CCTS benchmarks; identify quick‑win abatement (waste‑heat, energy efficiency).
|
| Q4 2025 |
Sign up for a digital MRV pilot—Anaxee or equivalent—to de‑risk data gaps.
|
| Q1 2026 |
Develop an internal carbon price aligned with expected CCC range (₹200–300/t).
|
| Q2 2026 |
Engage with BEE on methodology consultations—lobby for sector‑specific nuances.
|
| Ongoing |
Track EU CBAM charge calculator; re‑negotiate export contracts based on embedded carbon.
|
13. Policy Recommendations (Straight Talk)
- Transition Coal Cess into a True Carbon Tax
Hypothecate proceeds to a Price‑Stability Fund for CCCs rather than general revenue. - Introduce a Price Collar
Floor ₹150, ceiling ₹600/t to avoid the REC‑type boom‑bust. - Fast‑Track Scope‑3 Methodologies
Especially for agriculture and logistics—critical to decarbonise rural supply chains. - Integrate with GST IT Backbone
Automate certificate retirement and penalty collection through existing e‑invoice rails. - Build a CBAM‑Readiness Portal
Public carbon‑intensity disclosure for exporters; makes customs paperwork smoother.
14. The Road Ahead: Intensity Today, Absolute Caps Tomorrow?
India’s rate‑based ETS is a start, not an end. The net‑zero 2070 goal will eventually require tonnage caps and negative‑emission pathways (biochar, DAC). Expect:
-CCTS Phase 2 (2028‑30): Expand to shipping and aviation bunkers.
-Cap‑Hybrid by 2032: Combine intensity with sectoral caps once GDP growth stabilises below 6 %.
-International Linkages: Potential pilot linkage with Singapore’s carbon market for tokenised credit swaps.
15. Conclusion
Carbon pricing in India is no longer an academic debate. With the CCTS clock ticking and CBAM looming, the cost of carbon will soon appear on every corporate ledger—either as a tradable certificate, an import tax, or a reputational hit. Companies that invest early in credible data, verifiable reductions, and community‑positive offsets will not just dodge penalties; they’ll gain an export edge and access to cheaper green capital.
For players like Anaxee, the opportunity is to convert last‑mile execution expertise into the plumbing that India’s carbon market desperately needs. Data is the new oil, but in carbon pricing, data is the new oxygen—without it, nothing survives.
Call to Action
Ready to future‑proof your carbon strategy? Connect with us at sales@anaxee-wp-aug25-wordpress.dock.anaxee.com
About Anaxee:
Anaxee drives large-scale, country-wide Climate and Carbon Credit projects across India. We specialize in Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) and community-driven initiatives, providing the technology and on-ground network needed to execute, monitor, and ensure transparency in projects like agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, improved cookstoves, solar devices, water filters and more. Our systems are designed to maintain integrity and verifiable impact in carbon methodologies.
Beyond climate, Anaxee is India’s Reach Engine- building the nation’s largest last-mile outreach network of 100,000 Digital Runners (shared, tech-enabled field force). We help corporates, agri-focused companies, and social organizations scale to rural and semi-urban India by executing projects in 26 states, 540+ districts, and 11,000+ pin codes, ensuring both scale and 100% transparency in last-mile operations.
Ready to collaborate on your next Climate or Carbon project?
Email us at: sales@anaxee-wp-aug25-wordpress.dock.anaxee.com