Clean-cooking projects can produce high-integrity emission reductions (ERs) only when developers solve three hard problems together: a defensible baseline, objective evidence of sustained adoption (not just distribution), and an audit-grade MRV system. Newer methodologies and MRV guidance now favour metered and sensor-backed approaches (VM0050, Gold Standard’s metered methodology, and Clean Cooking Alliance templates). Ignore this shift — rely on surveys alone — and your credits will be risky, discounted, or invalidated. If Anaxee designs projects around measurable sustained use (SUMs + meters), solid additionality evidence (especially in India’s PMUY context), and conservative accounting, the results are bankable and valuable to buyers.
1. Why clean cooking still matters (and why carbon finance is useful)

Around the world, billions cook on polluting fuels (wood, charcoal, dung, kerosene). The harms are multiple: household air pollution and associated health burdens (disproportionately on women and children), time lost collecting fuel, pressure on local biomass stocks, and greenhouse gas emissions from inefficient combustion. In India, policy has massively expanded LPG access through programmes like Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY), but access frequently does not equate to exclusive or sustained use — stove-stacking (using multiple cook technologies) is common. That gap — converting access into sustained clean-fuel use — is precisely where targeted carbon finance can help by underwriting behaviour-change, refills affordability, or technology maintenance. But funds must be tied to measurable, verifiable outcomes.
2.What clean-cooking carbon projects are actually selling
These projects sell avoided emissions — reductions in GHGs compared to a baseline where households continue to use more carbon-intensive fuels or inefficient stoves. Important clarifications:
-These are not carbon removals; permanence concerns are about sustained use, not geological storage.
-Credibility rests on additionality (would the reduction have happened without the project?), accuracy (are the reductions measured correctly?), and traceability (is there a clear audit trail of evidence?).
-Standards now require higher measurement fidelity; metered and stove-sensor approaches are fast becoming the preferred path for high-integrity claims.
3. Major project archetypes and their measurement implications

Not every cookstove project is the same. Each model has distinct MRV needs and transaction costs.
Improved biomass cookstoves (ICS) — cheaper hardware replacing open fires. MRV challenge: objectively proving sustained use, since distribution often vastly overstates actual emission reductions.
Fuel-switch projects (LPG, electricity, biogas) — replace biomass/fossil fuels with cleaner fuels. MRV challenge: demonstrate sustained fuel consumption (refill frequency, electricity kWh, or biogas production/use). Metering/purchase logs are high-value evidence.
Advanced biomass & pellets — require supply-chain documentation to ensure feedstock sustainability and avoid leakage.
Community-scale biogas — methane capture + use; MRV must quantify substitution versus baseline manure handling and open-fire use.
Higher measurement fidelity (meters, SUMs) usually increases costs but reduces uncertainty and raises buyer confidence — and thus price.
4. Baseline and additionality: the real accounting work
Baselines capture the counterfactual — what households would have done absent the project. With stove-stacking common, a naive baseline (e.g., “this household had a smoky stove”) is not enough. Typical baseline approaches:
-Survey-based baseline: household-reported fuel use and stove types. Cheap but prone to social-desirability and recall bias.
-Observed baseline: enumerator observation of stove type and fuel stores. Useful but limited for quantifying hours-of-use.
-Metered baseline: where possible (LPG refills, electricity meters), provides objective consumption history. Preferred when feasible.
Additionality in India is the hard edge-case because PMUY and related subsidies have changed the policy landscape. PMUY has delivered tens of millions of LPG connections — the program data show very large coverage and rising refill rates — which means carbon projects must demonstrate additional behaviour (e.g., increased refill frequency, bridging affordability gaps, stimulating exclusive use, or targeting households not reached by government programmes). Relying on distribution of an LPG cylinder alone without proving sustained refills will not pass muster. Use government data to justify your additionality assumptions and be conservative.
5. The MRV reality: what verifiers now expect

Standards (Verra, Gold Standard) and the Clean Cooking Alliance have moved decisively toward objective measurement. The key MRV components every credible project must have:
5.1 Stove Use Monitors (SUMs)
SUMs — small temperature/data loggers affixed to stoves — objectively record stove usage events and durations. They are the most defensible way to demonstrate ongoing use for non-metered stoves. Deploy SUMs on a statistically valid, stratified sample and combine with surveys to extrapolate to the whole cohort. SUMs help detect a Hawthorne effect, tampering, and temporal adoption patterns. Clean Cooking Alliance protocols explicitly recommend SUMs as best practice for usage verification.
5.2 Metered approaches for fuel-switch projects
For LPG or electrical cooking projects, purchase records, cylinder refill logs, or electricity meters are the best evidence. Gold Standard’s metered methodology and Verra’s VM0050 explicitly recognise and prefer metered data where feasible because it significantly reduces uncertainty. If you operate in a PMUY context, work with refill retailers or LPG OMCs to access anonymised refill frequency data for beneficiaries where possible.
5.3 Surveys, KPTs and CCTs
Kitchen Performance Tests (KPTs) and Controlled Cooking Tests (CCTs) remain useful for labelling device efficiency and translating device performance into fuel savings under controlled conditions. But field-level sustained use needs SUMs/meter evidence, backed by representative household surveys capturing stacking behaviour and qualitative reasons for non-use. Standards increasingly require the mixed-method approach: sensors + surveys + purchase records.
5.4 Sampling design and QA/QC
Design your sampling to meet verifier confidence thresholds. Use stratified random sampling by socio-economic status, geography, household size, and initial baseline stove/fuel type. Train enumerators intensively, keep GPS-tagged photos, and maintain raw data files with version control. Verifiers will demand original SUMs logs, raw survey forms, enumerator training records, and a documented data cleaning process — so treat data management as a compliance function, not an afterthought.
6. A practical MRV protocol (copy-paste-ready checklist)

This is operational — adopt it and modify per project specifics.
Monitoring schedule
-Baseline: SUMs (sample) + survey (full) + fuel purchase data collection (if available).
-Early follow-up: 3 months post-distribution (adoption signals).
-Core monitoring windows: 6, 12, 24 months (SUMs + surveys).
-Annual reporting thereafter; scheduled SUMs redeployments for sample refresh every 18–24 months.
Data to collect
-Raw SUMs temperature logs (time-stamped).
-Fuel purchase/refill receipts or utility meter logs.
-Household survey results (baseline and follow-ups).
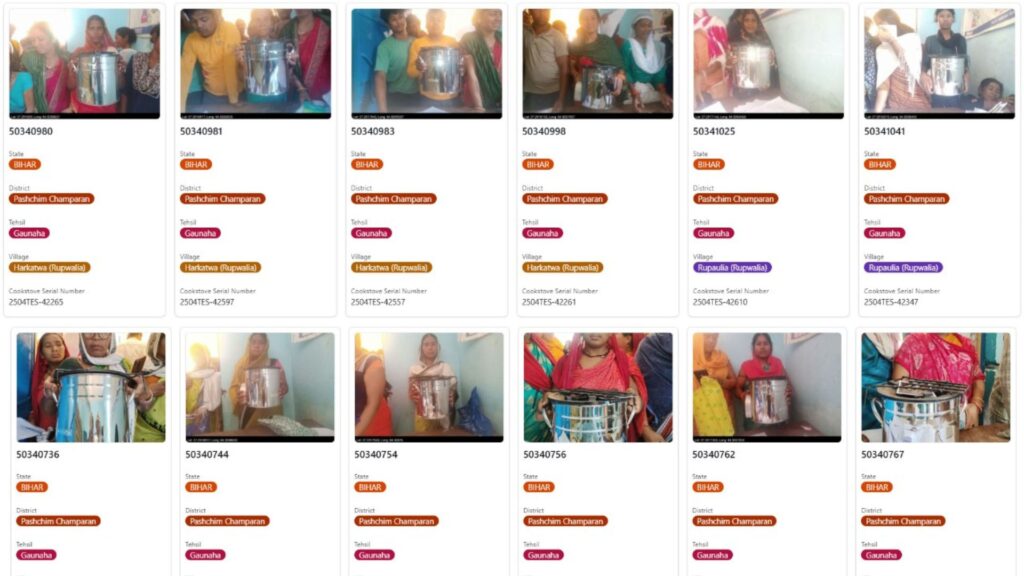
-Pictorial proof (GPS-tagged photos) and enumerator visit logs.
-Device serial numbers, beneficiary registry, installation logs.
Quality assurance
-Double-entry or automated ingest from SUMs into central repository.
-Supervisor spot-check on 10% of visits.
-Tamper-detection (SUMs battery/connection checks) plus periodic device recalibration.
-Maintain an audit folder with all raw and derived files for VVB access.
Use this as your MRV spine and then add PDD-specific formulas, e.g., substitution factors, emission factors, and conversion tables.
7. Risk, integrity, and the reputational minefield
Cookstove carbon credits faced strong academic and media scrutiny for overstated claims in the past. That scrutiny forced standards bodies and the Integrity Council (ICVCM) to raise the bar — rejecting simplified, survey-only methodologies and favouring metered/measured approaches. If your project relies on distribution records or optimistic usage assumptions without sensor or meter backing, expect deep discounting or rejection by high-integrity buyers. Conservative accounting and transparent evidence are not optional — they are business hygiene.
Common failure modes and countermeasures:
-Distribution ≠ use: countermeasure — conditional payments tied to verified use (SUMs/meter evidence).
-Double-counting with government programmes: countermeasure — explicit PDD documentation showing how your intervention goes beyond government provision (e.g., refill subsidies, maintenance, user training targeting refill behaviour).
-Sample bias and social desirability: countermeasure — objective sensors, independent enumerators, and careful sampling.
-Under-budgeting MRV & VVB costs: countermeasure — model verification cycles early and build VVB engagement into project timelines and budgets.
8. Operational blueprint: from procurement to verified credits
A carbon-grade cookstove programme is first and foremost an operational delivery challenge. Below is a sequence that reduces MRV friction and raises buyer confidence.
Pilot and acceptability testing: test device fit for purpose (user ergonomics, fuel needs, cooking styles). Document pilot KPTs/CCTs and field user feedback.
Procurement & performance certification: procure devices with lab performance certificates (WHO or Clean Cooking Alliance ratings). Retain test reports and device warranty info.
Beneficiary registry and unique IDs: register beneficiaries with GPS, ID, device serial numbers, and signed consent forms. This registry is the backbone of traceability.
Distribution + user training: ensure each household receives hands-on training. Capture attendance and photo proof.
MRV deployment: deploy SUMs/metering devices on a validated sample and collect baseline purchase/consumption evidence. Keep raw files in a version-controlled repository.
Post-distribution follow-up & maintenance: scheduled visits at 3, 6, 12 months with maintenance support. Use conditional incentive payments to encourage verified use.
VVB engagement & pre-audit: bring in an independent verifier early to review MRV protocols and pilot data — this reduces rework at validation.
If any of these steps are skipped, you increase risk of audit friction and potential invalidation.
9. Budget reality check (be conservative)
Many projects misprice themselves by underestimating MRV and verification costs. A realistic split:
-Hardware & distribution: 40–55%
-Behaviour-change & after-sales: 10–20%
-Monitoring & MRV (incl. SUMs/metering): 10–25%
-VVB & verification cycles: 8–15%
-Programme management & contingency: 5–10%
If you trim MRV to save costs, you will likely lose more in discounts or failed validations. Build MRV and VVB costs into the unit economics up front.
10. Commercialisation: what buyers will and won’t pay for
Buyers have become pickier. What commands a premium:
-Conservative, sensor-backed ERs. Sensors/metering reduce uncertainty and attract quality buyers.
-Transparency & audit trails. Raw SUMs logs, sample survey files, and enumerator training records available on request.
-Co-benefit evidence. Documented health outcomes, time savings, and gendered benefits enhance buyer interest in impact-oriented portfolios.
-Additionality clarity. Show how the project adds beyond government programmes (e.g., refill affordability or exclusive-use incentives where PMUY provided hardware).
Buyers will discount or avoid projects that rely exclusively on distribution or surveys and cannot produce raw sensor/meter files.
11. Aggregation & programme-based registration: scale without losing discipline
Small projects are uneconomic if each carries full VVB costs. Aggregation (pooling multiple small interventions under a programme approach) makes sense — but governance is everything: who signs sales contracts, how are revenues split, and how is the MRV protocol consistently enforced across geographies? Registries support programmatic registration, but you must standardise PDD templates, a central MRV repository, and a single governance charter for subprojects. Do this well and you lower per-credit costs and increase buyer appetite.
12. Practical PDD/MRV wording (audit-ready samples)
Use these clauses to speed PDD drafting and reduce back-and-forth with verifiers.
Monitoring objective (sample)
“The project quantifies sustained adoption of Project stoves and fuel-switch behaviour using a mixed-method monitoring system combining Stove Use Monitor (SUMs) data from a stratified, representative sample, fuel purchase/refill records where available, and annual socio-economic household surveys. All raw SUMs logs, survey instruments and enumerator training materials are retained in the project MRV repository and made available to the VVB upon request.” Clean Cooking Alliance
Additionality rationale (sample)
“The project targets households that, despite receiving connection under national programs, demonstrate low refill frequency and high stove-stacking. By providing targeted refill affordability support, user training, and maintenance incentives that exceed government program provisions, the project increases sustained use of clean fuel — thereby producing measurable additional emission reductions.” (Cite PMUY coverage and refill trends.)
Use conservative factors and avoid optimistic extrapolations.
13. A compact Anaxee playbook — what to do next (practical & unapologetic)
If Anaxee wants to scale credible clean-cooking credits in India, focus on:
Design for measurement: pick technologies and distribution models that support metering or reliable SUMs deployment. Meter when you can; use SUMs when you can’t.
Solve refill economics: in PMUY contexts, the marginal gain is sustained refills. Design top-up/subsidy interventions tied to verified refill behaviour.
Build a central MRV hub: centralise data ingestion, cleaning, and audit folders. Train enumerators thoroughly and maintain version-controlled raw data.
Aggregate from day one: standardise PDD templates and MRV protocols so small cohorts can be pooled under a single program.
Conservatism & transparency: err conservative in ex-ante estimates; publish methodological choices and make samples available to buyers.
Be brutal about quality control: it’s cheaper to do MRV properly than to defend inflated claims later.
14. Hypothetical pilot: a design you can replicate
Target cohort: 10,000 rural households across two districts with demonstrable low refill frequency.
Intervention: partial LPG refill subsidy for 12 months + intensive behaviour-change + SUMs on a 10% representative sample.
MRV plan: baseline SUMs + survey; SUMs redeployment at 6 and 12 months; monthly refill logs for the cohort from retail partners where feasible; independent verification at 12 and 24 months.
Commercial packaging: conservative ex-ante ERs, buyer quarterly reporting with access to anonymised SUMs sample, and a 5–10% buffer for programme risk.
This pilot balances costs and credibility and produces a buyer-friendly evidence package.
15. Buyer due diligence checklist (for corporates)
Before you sign a purchase agreement, demand:
-Raw SUMs files for representative monitoring windows and a sample of cleaned extracts.
-Clear additionality evidence against national/local programmes (e.g., PMUY stats and how the project adds to those).
-Benefit-sharing and grievance redress mechanism documentation.
-Sample verification report from a VVB and contactable references.
-Evidence of supply-chain sustainability if biomass/pellets are used.
If a developer can’t provide these, discount the credits or walk away.
16. Closing reality check (no marketing spin)
Clean cooking is high-impact and can produce high-integrity ERs — but only if project developers stop treating carbon income as a rebate on distribution costs. The market has shifted. Standards and buyers now reward measurement (metering and SUMs), conservatism, and transparency. Anaxee’s operational strengths — local field teams, dMRV capacity, and experience in community engagement — are exactly the assets needed to execute credible programs. But execution must prioritise MRV funding and discipline. Skimp on monitoring and you’ll pay later in auditor delays, discounts, or stripped credits.
Connect with us at sales@anaxee.com