Nature-Based Carbon Solutions from India: Anaxee’s Tech for Climate Platform Powers Scalable, Transparent Impact
The Problem Isn’t Ambition. It’s Execution.
In the fight against climate change, Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) are globally recognized as one of the most effective tools to reduce and remove greenhouse gas emissions. Yet, most NbS projects fail to scale because of one simple reason: they cannot be executed effectively at the last mile.
There is a yawning gap between corporate climate ambition and grassroots implementation.
This is exactly the problem that Anaxee’s Tech for Climate platform solves—by combining technology, people, and processes to deliver carbon impact from the remotest corners of India to the global carbon market.
Introducing Anaxee: India’s Climate Execution Infrastructure
Anaxee is building India’s largest last-mile outreach network with:
-
50,000 Digital Runners
-
Coverage in 26 states, 540+ districts, 11,000+ pin codes
-
A tech stack designed to execute and monitor NbS and community-based carbon projects
We call it: “Tech for Climate.”
It’s not just a buzzword- it’s our operating system for delivering climate action.
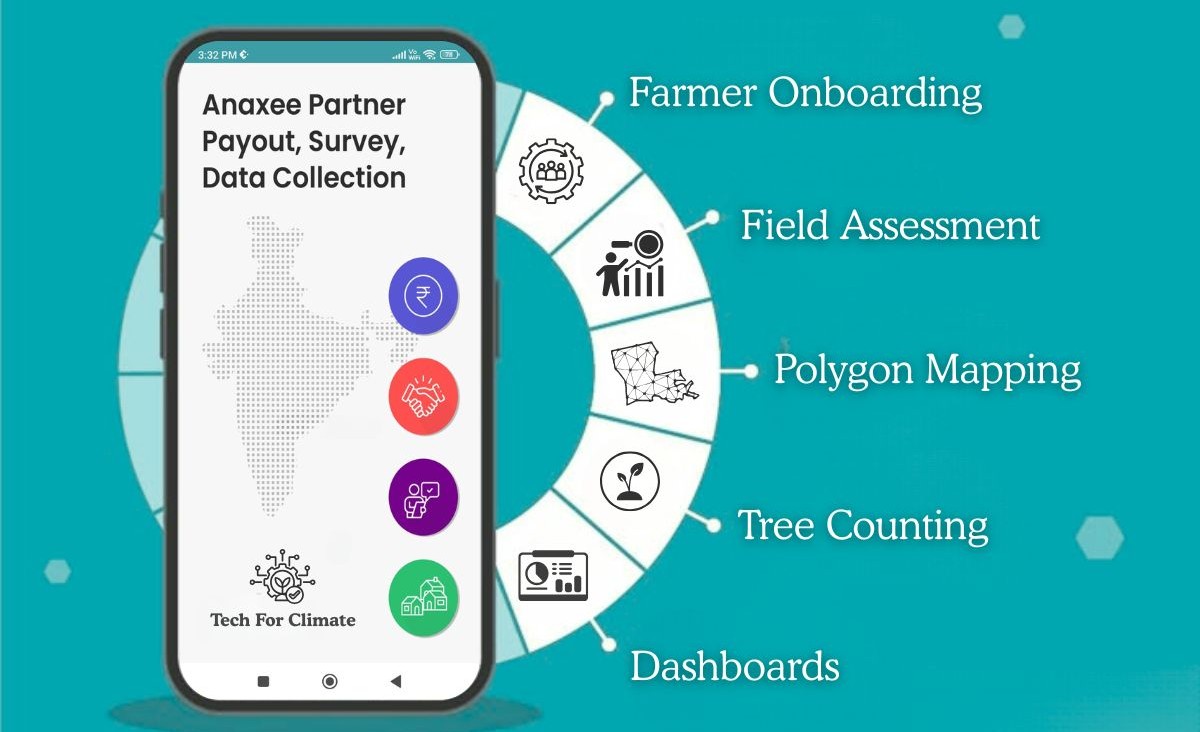
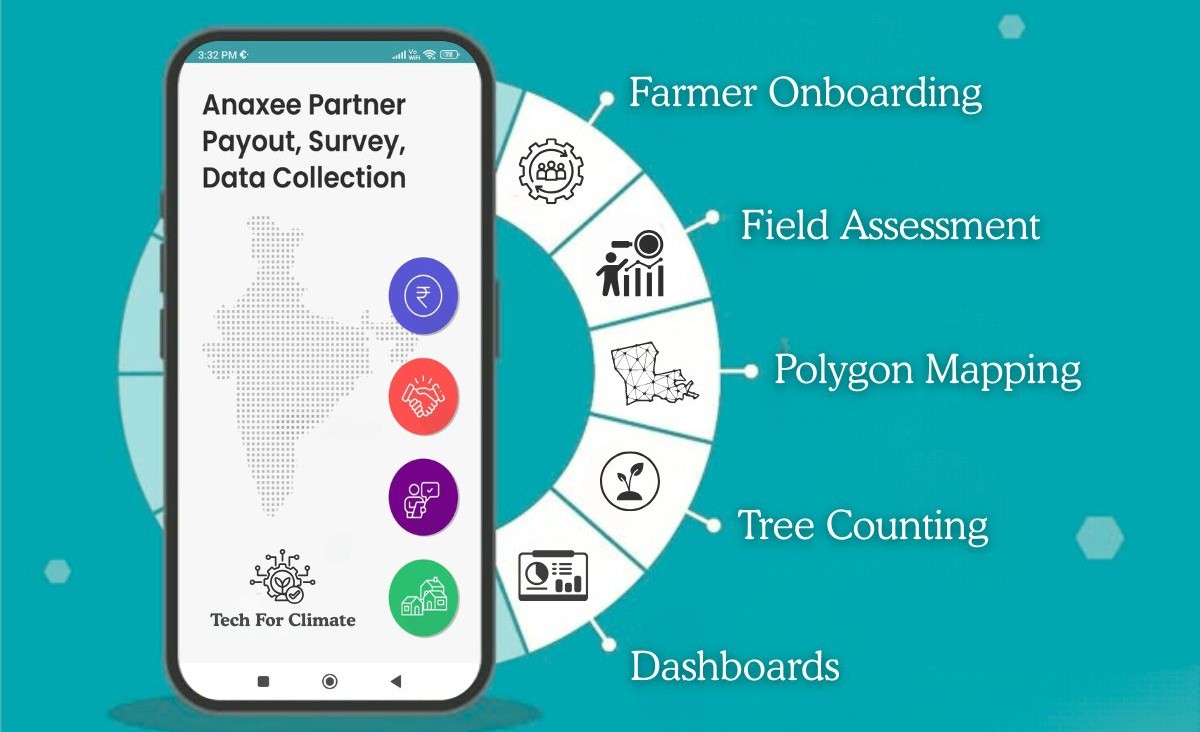
What is ‘Tech for Climate’?
Think of it as an end-to-end project execution engine for climate action:
– A digital + physical infrastructure that makes carbon projects scalable, monitorable, and community-anchored.
– Built to execute methodologies from Verra, Gold Standard, and CCTS India.
– Designed specifically for the complexities of India.

Core Functions of Tech for Climate
| Function | Details |
| REACH | Access to remote villages and communities through Digital Runners |
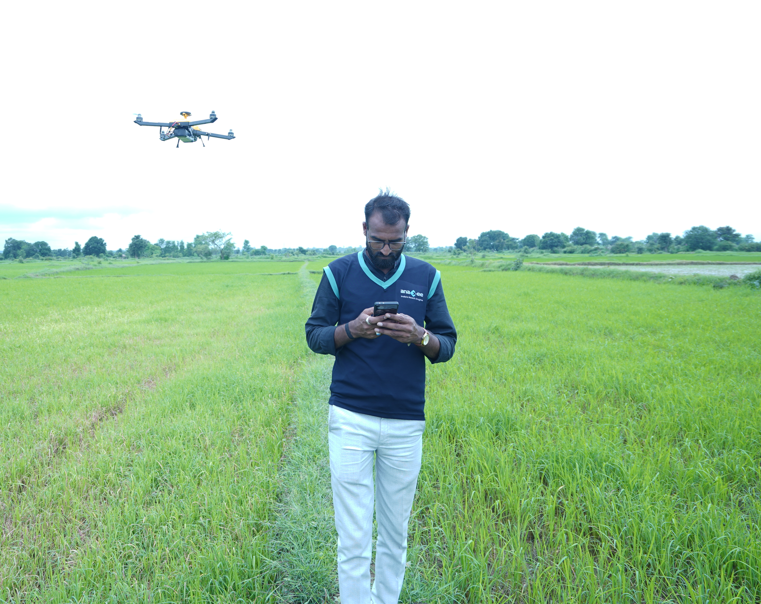
| DATA | GPS-verified, timestamped digital surveys & ground photos |
| TRUST | Transparent, tamper-proof documentation and live dashboards |
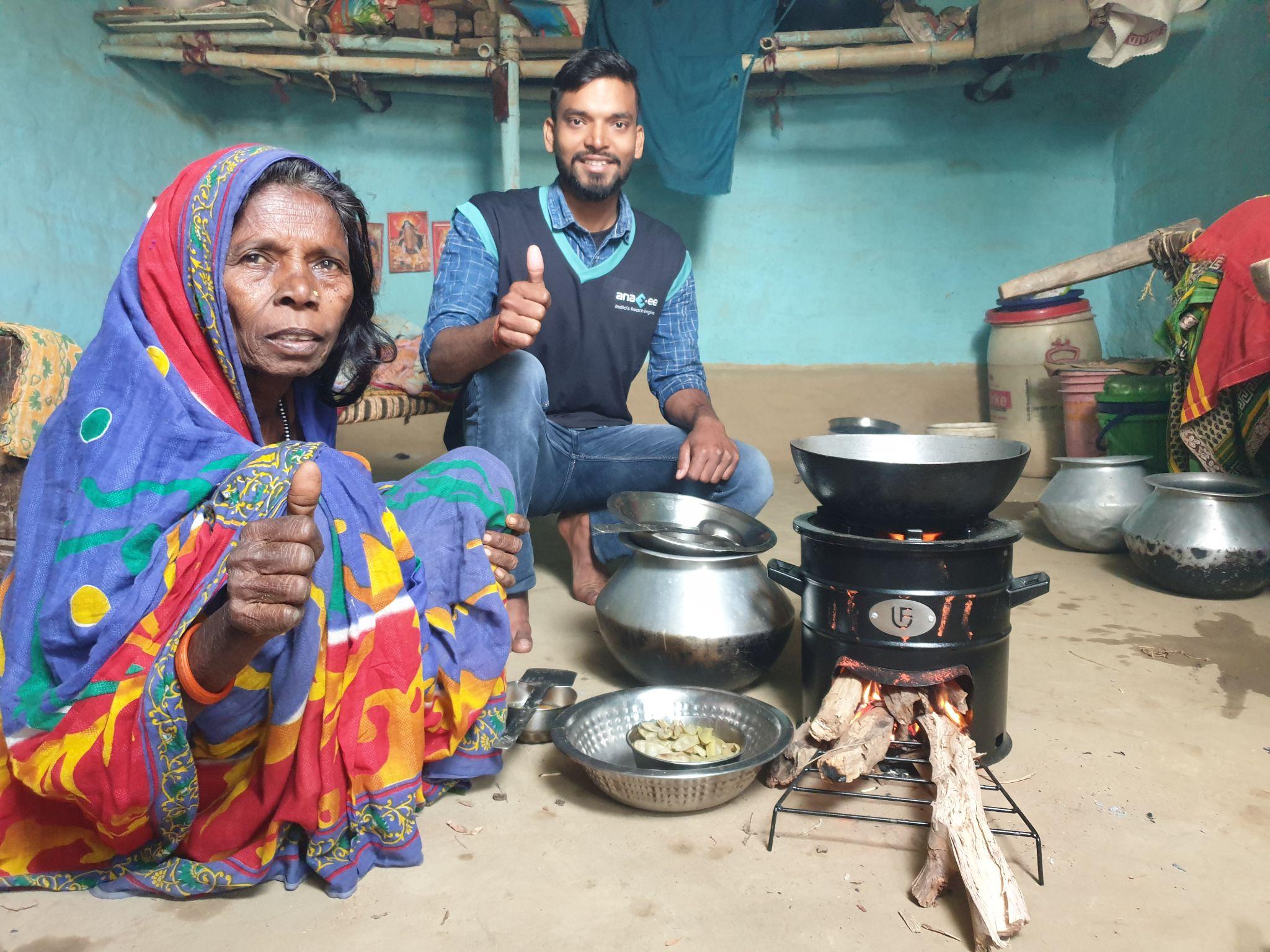
| EXECUTION | Bund planting, clean cookstoves, water filters, LED distribution at scale |
| INTEGRITY | Adherence to MRV standards of global carbon registries |
Why India Matters to the Global Carbon Market
India has:
– The land (underutilized bunds, fallows, and marginal plots)
– The people (smallholder farmers and tribal communities)
– The potential (to sequester gigatonnes of carbon through NbS)
But without infrastructure, technology, and trust, this potential remains untapped.
That’s where Anaxee becomes indispensable.
Execution at Scale: What Makes Anaxee Unique
Unlike traditional developers, Anaxee doesn’t just consult or design projects—we execute them on the ground.
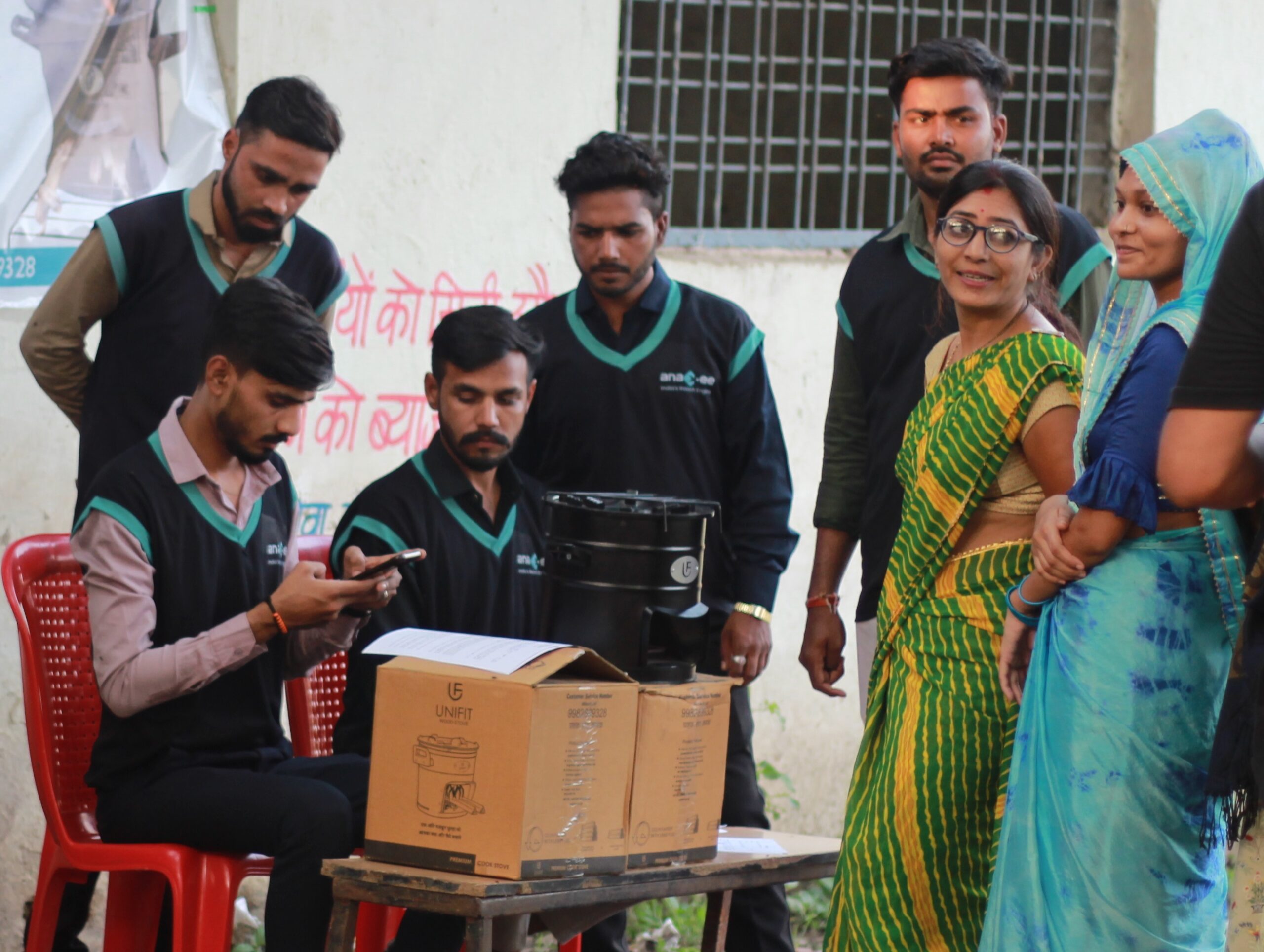

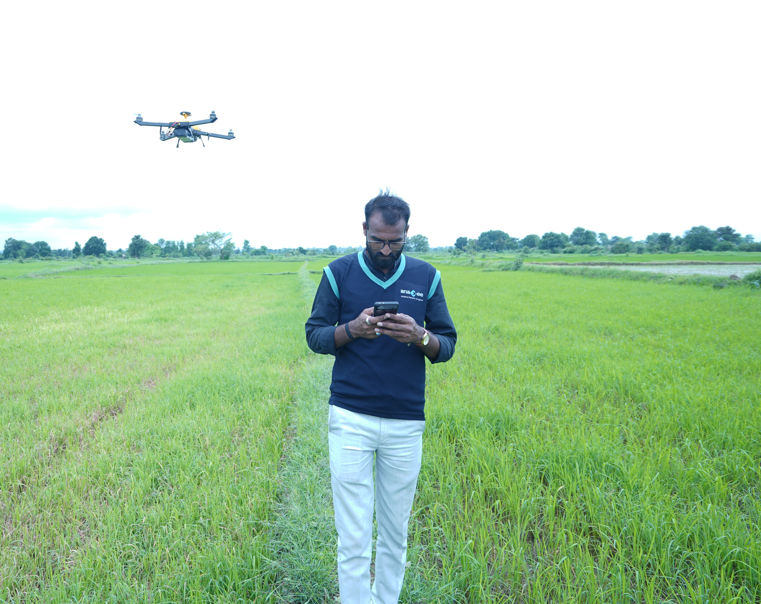
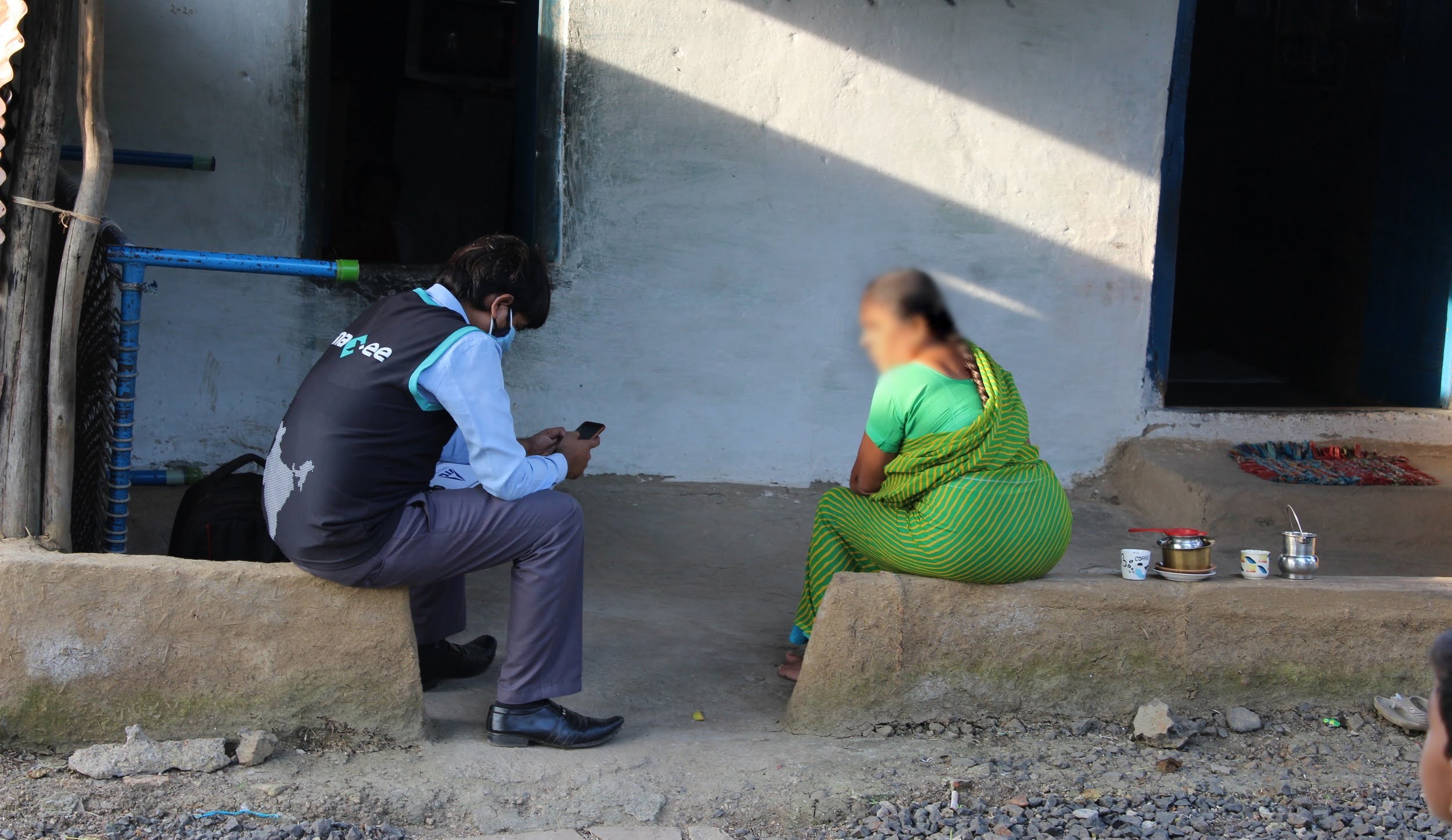
1. Digital Runners: Our Climate Foot Soldiers
Each Digital Runner is:
– Local, trained, and app-enabled
– Responsible for mobilizing farmers, conducting surveys, distributing assets
– Incentivized to ensure project success and MRV compliance
2. Platform Approach to MRV
We use:
– Mobile-first data collection
– Geo-fencing, timestamped images
– Unique IDs for farmers, plots, and devices
– Aggregated dashboards for real-time monitoring
This makes carbon credit issuance faster, cleaner, and trustworthy.
3. Multi-Methodology Execution
We’re not locked into a single method. Instead, our platform can execute:
– VM0047 (Agroforestry)
– AMS-II.G (Cookstoves)
– AMS-I.E (Solar devices)
– AMS-III.AV (Water filters)
– AMS-III.BB (LEDs)
We ensure every credit is rooted in reality.
Nature-Based Solutions: Grounded in Community, Verified by Tech
Anaxee understands that carbon is local, but markets are global.
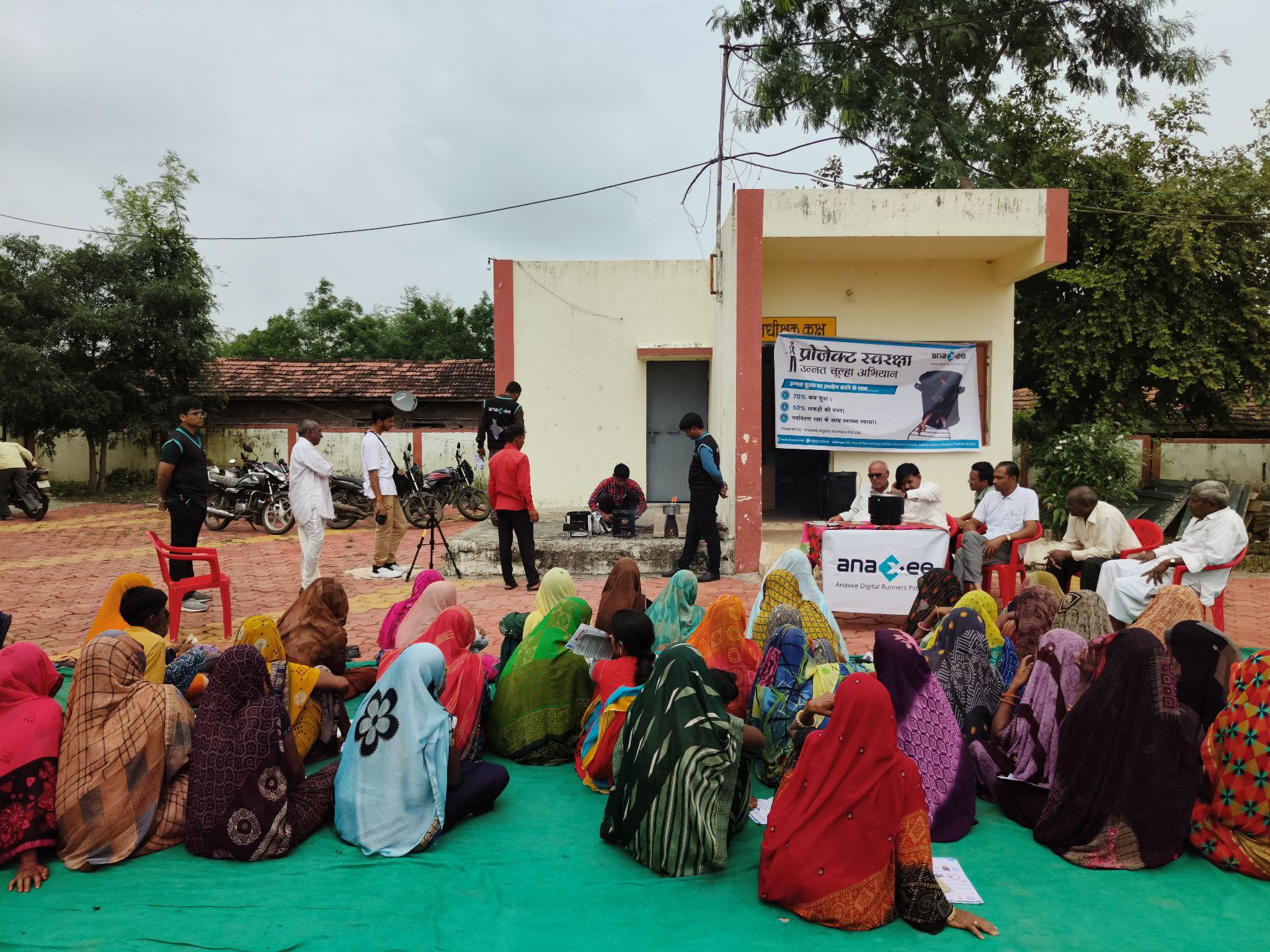
That’s why every nature-based intervention we run includes:
– Community Engagement Plans
– Free Asset Distribution or Co-benefit Sharing
– Livelihood Linkages
– Transparency with Village Leaders and Local Institutions
Project Types We Execute
| Type | Description | Co-benefits |
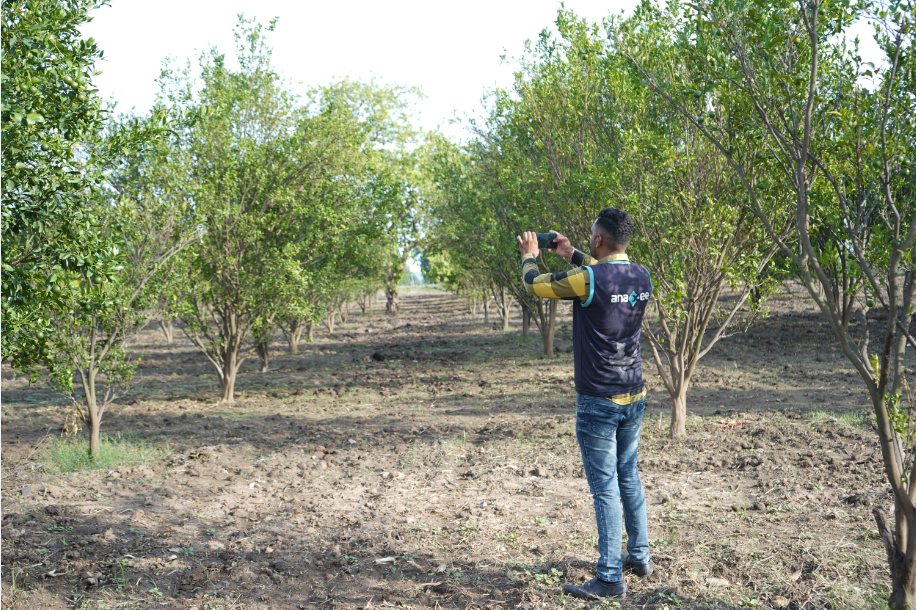
| Bund Agroforestry | Tree plantations along field boundaries | Soil health, income diversification |
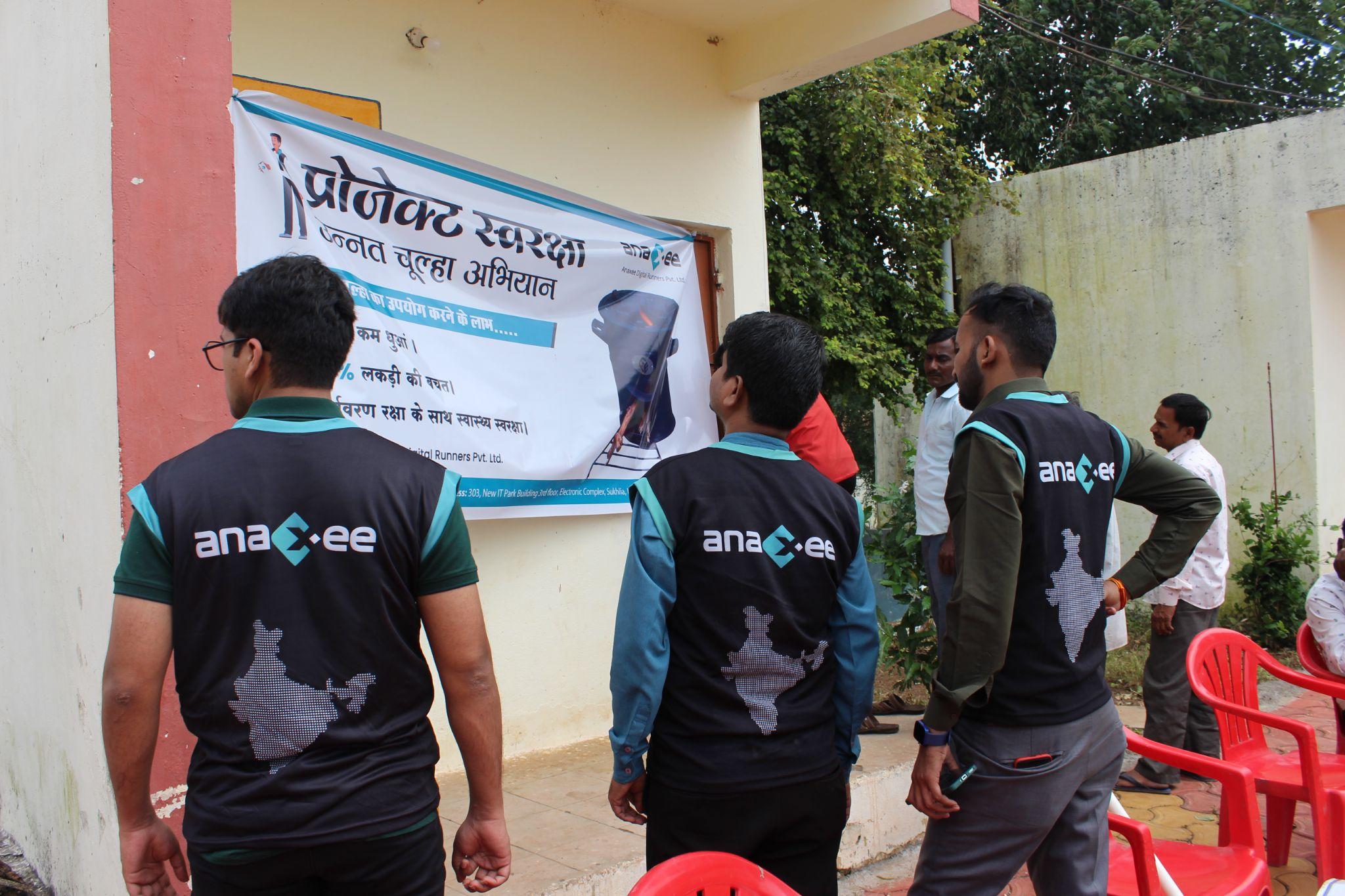
| Improved Cookstoves | Distribution of fuel-efficient stoves | Reduced indoor pollution, health |
| Solar Devices | Home lighting systems | Reduced kerosene use, savings |
| Water Filters | Portable purification units | Access to safe drinking water |
| LEDs | Ultra-efficient lighting | Energy savings, better visibility |
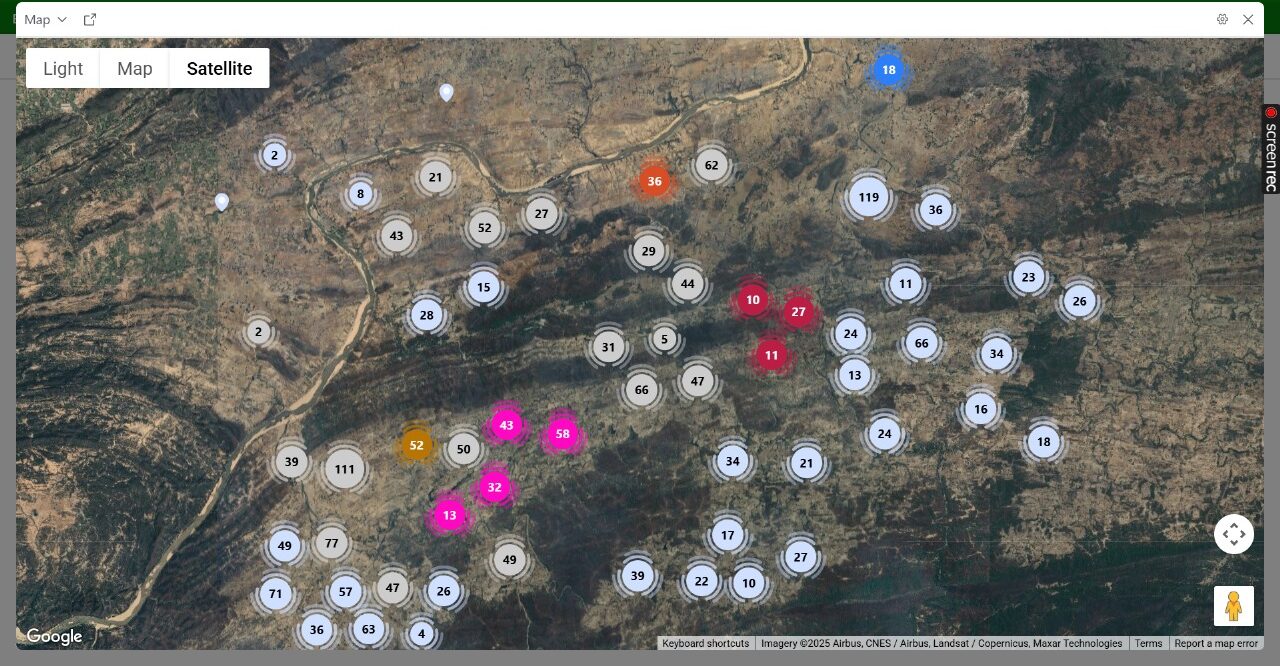
Project Locations: Our Footprint
We’re executing or planning nature-based carbon projects in:
– Madhya Pradesh (Agroforestry, Cookstoves)
– Chhattisgarh (Solar, Cookstoves, Water filters)
– Bihar (Cookstoves, Tree planting)
– Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra (Farmer outreach and bund plantation pilots)
With each project, our goal is to embed transparency, scale, and speed.
How We Deliver Value Across the Climate Value Chain
For Carbon Project Developers
– On-ground capacity
– Execution-as-a-Service
– Digitally structured monitoring
For Corporates & Carbon Buyers
– MRV-compliant, high-quality credits
– SDG co-benefits
– Transparent dashboards and traceability
For NGOs & Implementing Agencies
– Tech-powered scale
– Real-world data and feedback loops
– Reduced leakage and enhanced impact
For Local Communities
– Income from trees
– Free climate-smart assets
– Jobs as Digital Runners or nursery suppliers
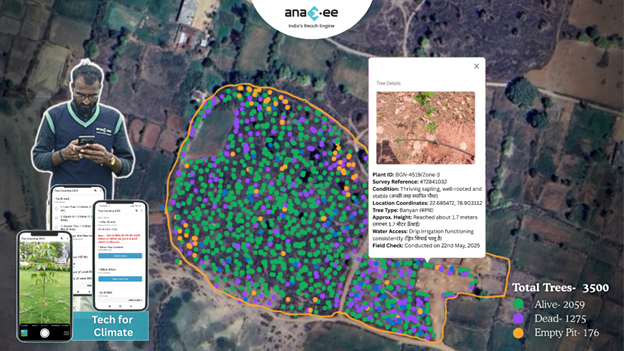
Digital Proof: Tech Ensures Integrity
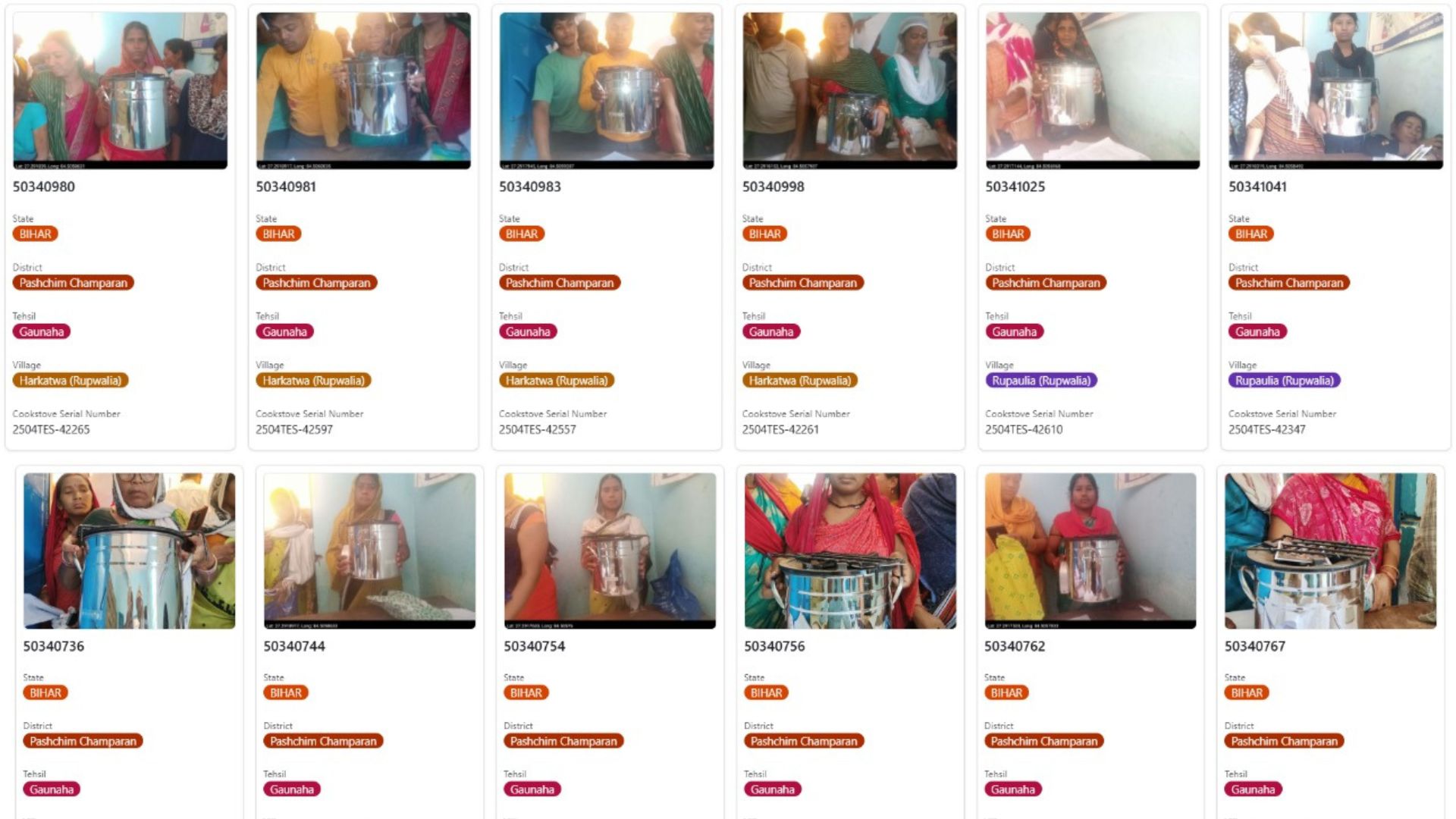
Every intervention in our projects is backed by digital proof:
– Tree planting with species count, farmer ID, and survival tracking
– Cookstove usage surveys, replacement verification, fuel wood savings
– LED distribution photos, GPS location, wattage records
No more unverifiable claims. No more ‘phantom carbon’. Just real climate action—digitally monitored.
Case Study: Agroforestry with Census-Based MRV in Central India
Anaxee has pioneered a census-based approach (vs. sample-based) for tree plantations:
– Every participating farmer is surveyed
– Every bund tree is counted, tagged, and digitally logged
– Ongoing survival rate updates via Digital Runners
This leads to:
– Lower credit rejection risk
– Higher buyer confidence
– More benefits to communities
Partnering with Anaxee: A Smarter Path to Credible Carbon
If you are:
– A carbon developer with methodology expertise
– A corporate under Net Zero pressure
– An NGO with community access
– A funder looking to support scalable impact
…then Anaxee can be your climate execution partner.
We bring the platform, the people, and the process.
You bring the vision. Together, we deliver impact.
Global Implications: Can India Power Global Net Zero?
Yes- if done right.
Anaxee’s model allows the Global North to fund and verify climate action in the Global South with unprecedented confidence.
And that’s what the future of carbon markets should look like:
Digitally verified, locally rooted, globally relevant.
Conclusion: Climate Action Needs Infrastructure. We Are Building It.
Most climate talk focuses on finance, carbon accounting, or blockchain.
But the bottleneck is in execution. And execution needs infrastructure- not just roads and drones, but human infrastructure too.
Anaxee’s Tech for Climate platform is that infrastructure. It’s how we turn:
– Ambition into impact
– Pilot into program
– Promise into proof