RFPs for Carbon Offset and Removal Projects: Global Tenders You Shouldn’t Miss

Carbon offset and removal projects are no longer just about good intentions. In 2025, they represent a rapidly growing procurement ecosystem, with companies, governments, and alliances issuing billion-dollar RFPs (Requests for Proposals) for high-quality, measurable climate outcomes. Whether you’re developing a biochar plant in India, an agroforestry bundle in Africa, or a reforestation project in Brazil, knowing where the money is can be half the battle.
If you’re a project developer or climate consultant, this post will help you navigate the top open calls globally. And if you’re looking for local-scale execution, monitoring, and tech-backed transparency, we’ll show you how Anaxee can help you win and deliver these climate contracts reliably.
Why Carbon RFPs Matter in 2025
Climate finance is getting more structured. While voluntary carbon markets once relied on one-on-one negotiations, today’s buyers—from Meta to Petrobras to the Government of Singapore—are issuing competitive RFPs with short deadlines, tough quality screens, and complex eligibility requirements. Most of these require:
– Strong MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification)
– Local stakeholder alignment
– Legal clarity around credit rights
– Proven ability to execute on the ground
Which is where Anaxee comes in.
How Anaxee Helps Developers Win RFPs
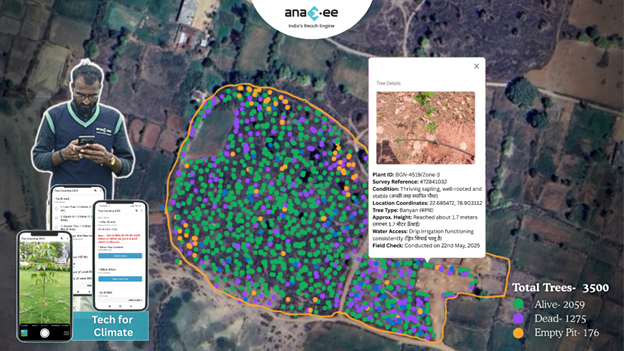
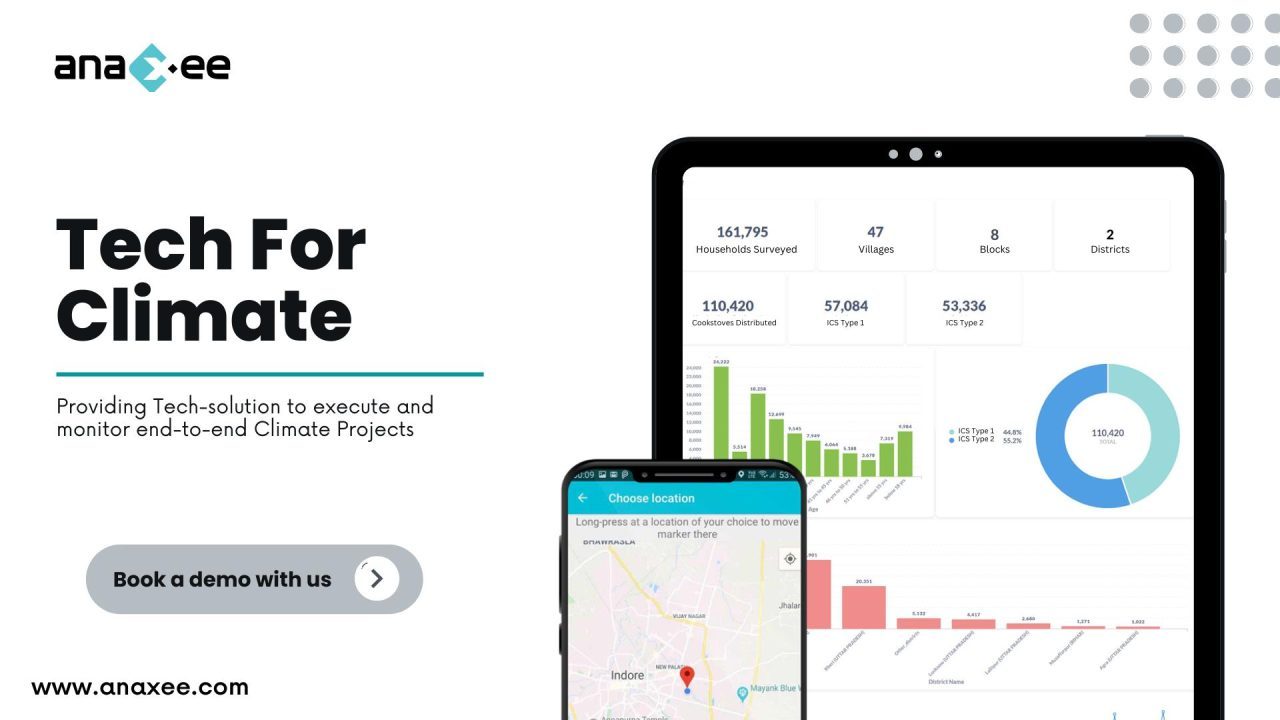
Anaxee is India’s largest last-mile climate execution engine. With a tech-enabled network of 50,000 Digital Runners active across 11,000+ pincodes, we provide exactly the kind of ground capacity, stakeholder engagement, and digital proof that global buyers and registries now demand.
Whether you’re submitting to an Article 6 government tender or a multinational like Microsoft, Anaxee can support:
– Field surveys and landholder onboarding
– Tree plantation, agroforestry layouting, and care
– IoT-integrated monitoring with GPS, timestamped data
– Village-level engagement with tribal councils and panchayats
We’re already delivering for clients in carbon cookstove rollouts, bamboo plantation baselines, and ARR methodologies like VM0047.
Top 13 Global Carbon Offset & Removal RFPs (Live as of July 2025)
Below is a curated list of high-quality RFPs for offset and removal projects, sorted by deadline. These are real, verified opportunities with strong funding partners behind them.
| # | Issuer | Geography | What They Want | Deadline | Source |
| 1 | Planet2050 | Global | Tech-based CDR (biochar, BECCS, etc.) | 22 Jul 2025 | Link |
| 2 | IUCN | Rwanda | Biodiversity-linked ARR/IFM design | 24 Jul 2025 | Link |
| 3 | PGCC | USA | Verified offsets + EACs | 14 Jul 2025 | Link |
| 4 | American Forests | USA (California) | Tribal engagement for reforestation | 31 Jul 2025 | Link |
| 5 | NYSERDA | USA (New York) | CCUS and low-carbon fuels | 31 Jul 2025 | Link |
| 6 | Petrobras | Brazil | Forest credit procurement | Mid-Jul 2025 | Link |
| 7 | Meta | Global | Scope-3 emission reductions | 18 Jul NDA / 19 Sep full | Link |
| 8 | Ordnance Survey UK | UK | Credit sourcing partnerships | Q4 2025 | Link |
| 9 | EY | Global | 1.2 Mt spot + forward VCUs | Rolling | Link |
| 10 | Singapore Govt | Global | Article 6-ready ITMO credits | Late 2025 | Link |
| 11 | Watershed | Global | 1 Mt carbon removals | Rolling | Link |
| 12 | Microsoft | Global | Durable CDR credits | Rolling | Link |
| 13 | Frontier Climate | Global | $500K-$50M prepurchase | Rolling | Link |
Key Trends Developers Should Watch
1. Government Buyers Want Article 6 Compliance
Singapore, Brazil, and others are now actively procuring ITMOs under the Paris Agreement. If your project has the legal ability to authorize those credits, you stand to gain from long-term, compliance-level pricing.
2. MRV Standards Are Tightening
Almost all major buyers now benchmark projects against ICVCM Core Carbon Principles, or rely on third-party ratings. Poor data quality or weak documentation can sink a bid, even if the project is viable.
3. Speed Matters
The average RFP window is just 20–30 days. You need a partner who can help you mobilize field surveys, social buy-in, and tech documentation fast. Anaxee’s existing local footprint lets us act within days, not weeks.
4. Big Buyers Prefer Portfolio Diversity
Meta, EY, and Watershed all sign deals with a mix of nature-based and engineered removals. If you only have one project type, consider co-bidding with complementary partners.
How to Prepare Before You Submit
To give yourself the best shot, here’s what should be ready before you start applying:
– A robust project design document (PDD)
– Proof of community or landholder consent
– Draft monitoring plan and MRV stack
– Optional: Pre-signed NDAs or registration forms (Meta, Watershed, etc.)
If any of that is missing, reach out to Anaxee. We have pre-built SOPs and documentation templates for:
– Tree selection and planting (VM0047)
– Biochar production and weighing (C-Sink)
– Community meetings and benefit-sharing (Gold Standard)
Closing Thoughts
Winning carbon RFPs in 2025 is no longer just about writing a good proposal. It’s about proving you can execute—credibly, quickly, and equitably. Whether it’s planting 10,000 bamboo seedlings across 6 districts or monitoring 200 cookstove households in tribal areas, execution risk is what funders fear most.
That’s why they love developers who partner with local engines like Anaxee. We make your bid bankable.
Need help applying to any of the RFPs listed above? Email us at sales@anaxee-wp-aug25-wordpress.dock.anaxee.com